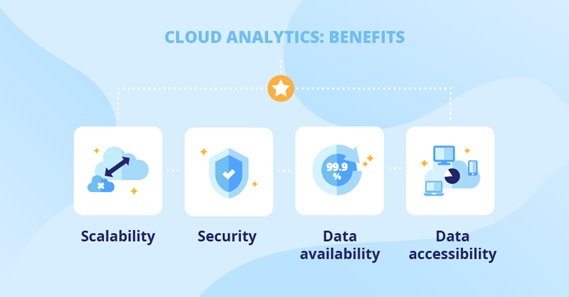
Benefits and types of Cloud Computing Scalability
Cloud scalability is used to handle the growing workload where good performance is also needed to work efficiently with software or applications. Scalability is commonly used where the persistent deployment of resources is required to handle the workload statically.[1]

Figure 1. the Benefits and Types of Cloud Computing Scalability
Figure 1 shows Scalability refers to the idea of a system in which every application or piece of infrastructure can be expanded to handle increased load.[2]
Benefits of cloud scalability
The major cloud scalability benefits are driving cloud adoption for businesses large and small:
- Convenience: : Often with just a few clicks, IT administrators can easily add more VMs that are available without delay—and customized to the exact needs of an organization. That saves precious time for IT staff. Instead of spending hours and days setting up physical hardware, teams can focus on other tasks.
- Flexibility and speed: As business needs change and grow—including unexpected spikes in demand—cloud scalability allows IT to respond quickly. Today, even smaller businesses have access to high-powered resources that used to be cost prohibitive. No longer are companies tied down by obsolete equipment—they can update systems and increase power and storage with ease.
- Cost savings: : Thanks to cloud scalability, businesses can avoid the upfront costs of purchasing expensive equipment that could become outdated in a few years. Through cloud providers, they pay for only what they use and minimize waste.
- Disaster recovery: With scalable cloud computing, you can reduce disaster recovery costs by eliminating the need for building and maintaining secondary data centers.[3]
Types of cloud scalability
It’s important to configure your cloud environment to best suit your needs. There are various types of scalability available to businesses, solving different scalability issues. These include:
Vertical scaling
Vertical scaling is also known as scaling up (or down). It means resizing an existing resource with no change to your code. You’re simply running the same code on a higher- or lower-spec machine.
When you scale vertically, you enlarge or diminish a resource to change the capacity of your existing infrastructure. That infrastructure becomes more or less powerful.
Horizontal scaling
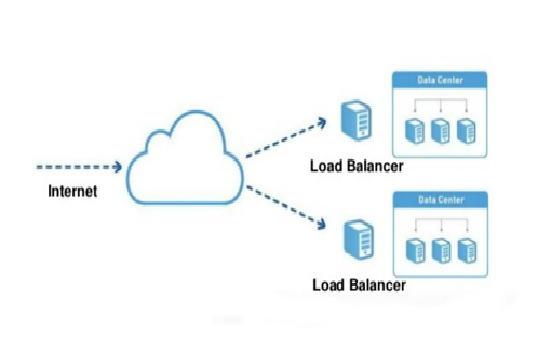
Horizontal scaling also goes by the name scaling out (or in). When your business scales horizontally, you add or remove instances of a resource or infrastructure. It involves breaking a sequential piece of logic into smaller pieces. That’s then executed in parallel across multiple resources or infrastructures.
With Amazon Web Services (AWS), an example of horizontal scaling is changing the number of nodes in a computing system. The size of each individual node remains the same.
Horizontal scaling is more labor-intensive than vertical scaling. It’s particularly important for organizations with high availability services requiring minimal downtime.
Diagonal scaling
Diagonal scaling refers to a combination of vertical and horizontal scaling. Your business grows vertically within existing infrastructure until it reaches a tipping point. At that stage, you add more resources to scale out horizontally.[4]
References:
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/scalability-and-elasticity-in-cloud-computing/
- https://acloudguru.com/blog/engineering/scalability-cloud-computing
- https://www.vmware.com/topics/glossary/content/cloud-scalability
- https://www.netguru.com/blog/cloud-computing-scalability
Cite this article:
Thanusri swetha J (2021), Benefits and Types of Cloud Computing Scalability, AnaTechMaz, pp. 19