Cloud Service Models
Cloud computing services come mainly in three types of service models: SaaS (Software as a Service), IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), and PaaS (Platform as a Service). Each of the cloud models has its own set of benefits that could serve the needs of various businesses.[1]
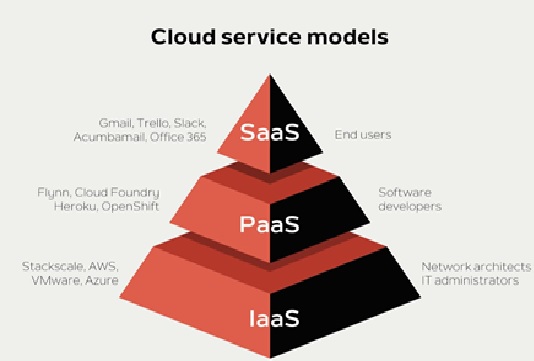
Figure 1. The Cloud Service Models
Figure 1 shows Cloud Services are among the most in-demand services recently, with big organizations like Microsoft, Google, Amazon, Oracle driving the path for innovation development. Rather than depending on their own private servers, organizations incline toward contracting out the storage to reputable providers, ignoring the obligation regarding supporting the foundation and guaranteeing security.[3]
Types of Cloud Services Models
Generally speaking, there are three basic types of cloud services:
Software as a Service (SaaS)
The most widely recognized type of cloud service is known as software as a service, or SaaS. This broad category encompasses a variety of services, such as file storage and backup, web-based email and project management tools.
Examples of SaaS cloud service providers include Dropbox, G Suite, Microsoft Office 365, Slack and Citrix Content Collaboration. In each of these applications, users can access, share, store and secure information in “the cloud.”
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a service, or IaaS, provides the infrastructure that many cloud service providers need to manage SaaS tools—but don’t want to maintain themselves. It serves as the complete data center framework, eliminating the need for resource-intensive, on-site installations.
Examples of IaaS are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure and Google Compute Engine. These providers maintain all storage servers and networking hardware, and may also offer load balancing, application firewalls and more. Many well-known SaaS providers run on IaaS platforms.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
The cloud service model known as platform as a service, or PaaS, serves as a web-based environment where developers can build cloud apps. PaaS provides a database, operating system and programming language that organizations can use to develop cloud-based software, without having to maintain the underlying elements.
Many IaaS vendors, including the examples listed above, also offer PaaS capabilities.[2]
The future of cloud services
As the availability of cloud services continues to expand, so will their applications in the corporate world. Whether a company chooses to extend existing on-premises software deployments or move 100% to the cloud, these services will continue to simplify how organizations deliver mission-critical apps and data to the workforce. From content collaboration and access control for employees to app delivery management and virtual desktop solutions for IT, plus a vast array of options in between, cloud services are transforming how people work and the ways businesses operate.[3]
References:
- https://www.fingent.com/blog/cloud-service-models-saas-iaas-paas-choose-the-right-one-for-your-business/
- https://www.citrix.com/en-in/solutions/digital-workspace/what-is-a-cloud-service.html
- https://k21academy.com/amazon-web-services/aws-solutions-architect/cloud-service-models/
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/future-of-green-computing/
Cite this article:
Thanusri swetha J (2021), Cloud Service Models, AnaTechMaz, pp. 25