Types of Cloud Deployment Model
A cloud deployment model is a specific configuration of environment parameters such as the accessibility and proprietorship of the deployment infrastructure and storage size. This means that deployment types vary depending on who controls the infrastructure and where it’s located. To make the most use of this computing type, a company should opt for a model that suits it best. To choose the right one for you, you’ll need to consider your computing, networking and storage requirements, available resources and business goals, as well as the pros and cons of cloud deployment models. [1]

Figure 1. The Types of Cloud Deployment Model
Figure 1 shows It works as your virtual computing environment with a choice of deployment model depending on how much data you want to store and who has access to the infrastructure. [2]
Types of Cloud Deployment Model
1. Public Cloud
The public cloud makes it possible for anybody to access systems and services. The public cloud may be less secure as it is open for everyone. The public cloud is one in which cloud infrastructure services are provided over the internet to the general people or major industry groups. The infrastructure in this cloud model is owned by the entity that delivers the cloud services, not by the consumer. It is a type of cloud hosting that allows customers and users to easily access systems and services. This form of cloud computing is an excellent example of cloud hosting, in which service providers supply services to a variety of customers. In this arrangement, storage backup and retrieval services are given for free, as a subscription, or on a per-use basis. Example: Google App Engine etc.
2. Private Cloud
The private cloud deployment model is the exact opposite of the public cloud deployment model. It’s a one-on-one environment for a single user (customer). There is no need to share your hardware with anyone else. The distinction between private and public cloud is in how you handle all of the hardware. It is also called the “internal cloud” & it refers to the ability to access systems and services within a given border or organization. The cloud platform is implemented in a cloud-based secure environment that is protected by powerful firewalls and under the supervision of an organization’s IT department. The private cloud gives the greater flexibility of control over cloud resources.[3]
3. Hybrid cloud
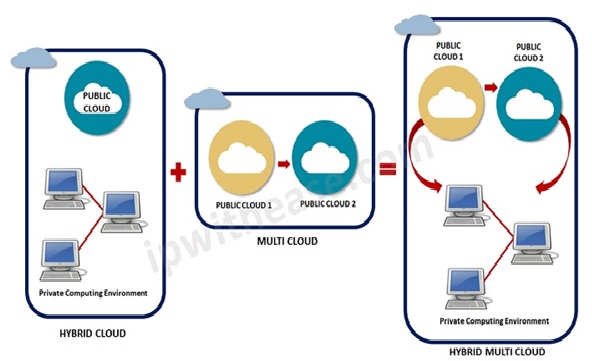
A hybrid cloud is a combination of two or more cloud architectures. While each model in the hybrid cloud functions differently, it is all part of the same architecture. Further, as part of this deployment of the cloud computing model, the internal, or external providers can offer resources. Let’s understand the hybrid model better. A company that has critical data will prefer storing on a private cloud, while less sensitive data can be stored on a public cloud. The hybrid cloud is also frequently used for ‘cloud bursting’. It means, suppose an organization runs an application on-premises, but due to heavy load, they can burst into the public cloud.[2]
4. Community cloud
It allows systems and services to be accessible by a group of organizations. It is a distributed system that is created by integrating the services of different clouds to address the specific needs of a community, industry, or business. The infrastructure of the community could be shared between the organization which has shared concerns or tasks. It is generally managed by a third party or by the combination of one or more organizations in the community. [3]
References:
- https://www.sam-solutions.com/blog/four-best-cloud-deployment-models-you-need-to-know/
- https://www.rishabhsoft.com/blog/basics-of-cloud-computing-deployment-and-service-models
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/cloud-deployment-models/
Cite this article:
Thanusri swetha J (2021), Types of Cloud Deployment Model, AnaTechMaz, pp. 29