The Future of Biomanufacturing
Biomanufacturing produces a wide range of biobased products for the emerging global bioeconomy. Biomanufacturing begins with bioprospecting – the discovery and commercialization of new products based on biologic resources. Biomanufacturing requires knowledge and methods from many scientific disciplines including biology, microbiology, biotechnology, chemistry, physics, engineering and technology. It includes genetic engineering and metabolic engineering plus various cell and tissue culture technologies.[1]

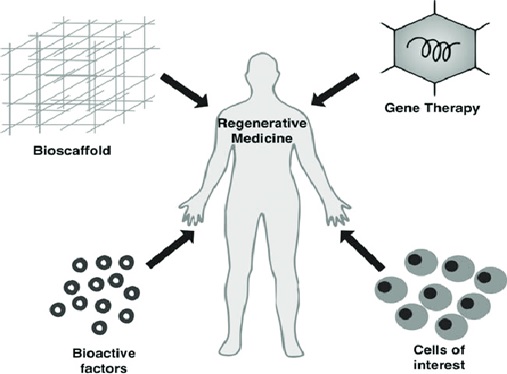
Figure 1. the future of Biomanufacturing
Figure 1 shows biomanufactured products range from biopharmaceuticals to industrial enzymes, human tissues and replacement organs, biofuels, ‘green’ chemicals and green products to replace those derived from petroleum. The application of biotechnology to industrial manufacturing is not only transforming how we develop and produce products, it's also generating new ideas - such as using microalgae to scrub power plant effluent gases and process water while making biofuels to help run the power plant at the same time. Another example is anaerobically turning cow manure and other wastes into gases to make electricity.[1]
Biomanufacturing Process Details
Biomanufacturing relies on naturally occurring processes and reactions to produce an output such as a material, product or chemical, to name a few that would normally be produced through a synthetic process. In a broad sense, nearly all manufacturing is based on the use of energy, such as heat, to change the form of something. It vastly reduces this energy requirement in favor of production through natural reactions.
Incredibly, the biological process on which nearly all biomanufacturing is based is fairly common one — fermentation. Fermentation makes use of naturally occurring microorganisms and enzymes to carry out reactions. It is the source of some of our most widespread food products, such as bread and beer. The functions and capabilities of fermentation have been no secret, as the process has been used for thousands of years.
As manufacturers search for ways to increase margins, boost sustainability and innovate in productivity, however, researchers and engineers have identified new and creative ways to use fermentation for manufacturing.
Some of the processes in which biomanufacturing can be involved are as follows:
- Raw material production, including plastics, paper and textiles
- Chemical production, using fermentation to develop soaps, detergents and more
- Energy production, generating power from biomass
- Food fortification and enhancement through natural processes as opposed to additives and preservatives
In the next section, we will take a broader view of the industries that are impacted by these functions.[3]
The Future of Biomanufacturing:
The biomanufacturing industry is undergoing a major shift, from single-product processes and stainless steel infrastructure to flexible, multi-product facilities using single-use technology. Though single-use is being widely adopted, there still exists a lag in automation and measurement to make the most use of the technology and data integration.[2]
References:
- https://www.biotech-careers.org/job-areas/biomanufacturing
- https://www.bioprocessonline.com/doc/the-future-of-biomanufacturing-0001
- https://www.advancedtech.com/blog/future-of-biology-in-manufacturing/
Cite this article:
Thanusri swetha J (2021), The Future of BioManufacturing, AnaTechMaz, pp. 22