Strengthening Telecom Networks Against Cybersecurity Threats
The rapid evolution of cybersecurity threats presents major challenges for telecom networks, particularly with the rise of 5G and other cutting-edge technologies. Reports show that Communications Service Providers (CSPs) face difficulties in identifying network vulnerabilities and preventing attacks. According to our latest Threat Intelligence Report, conducted in collaboration with Global Data, over 30 percent of CSP respondents reported experiencing eight or more breaches in the past year.

Figure 1. Fortifying Telecom Networks Against Cyber Threats.
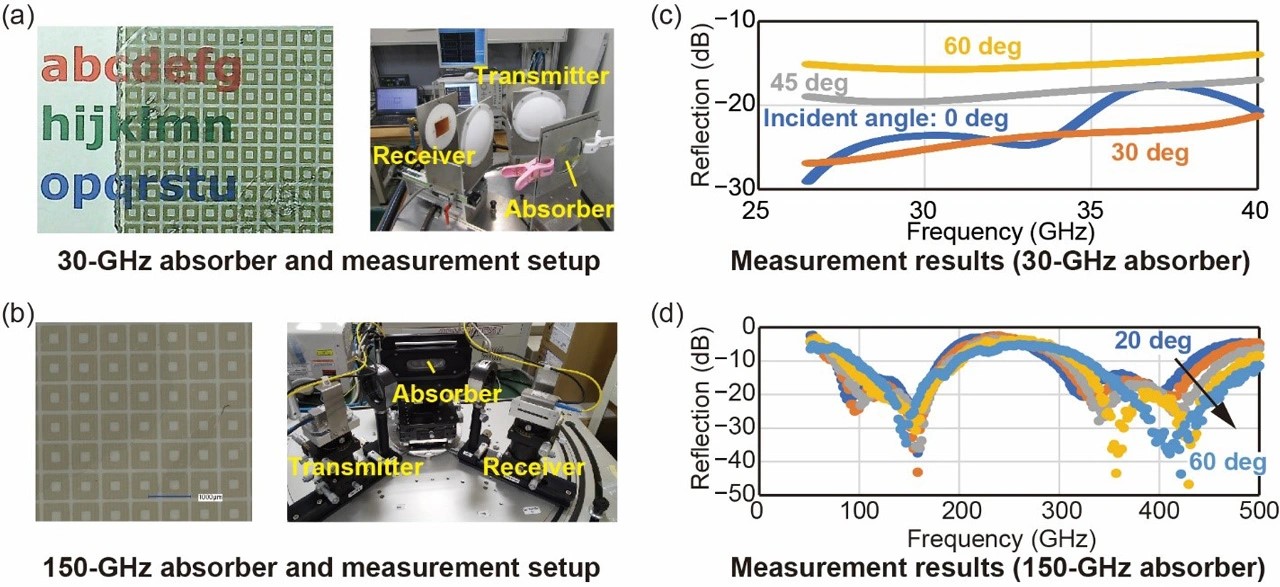
Advanced malware attacks, such as the Linux backdoor GTPDOOR—discovered by security researcher HaxRob—are designed for stealth operations within mobile carrier networks, exploiting vulnerabilities in the GPRS Roaming Exchange (GRX). These threats operate under the radar, blending in with routine network traffic and circumventing traditional defenses like firewalls. As hackers become increasingly skilled at evading detection, the need for strong, multi-layered security strategies is more critical than ever. Figure 1 shows Fortifying Telecom Networks Against Cyber Threats.
Why Telecom Operators Need Specialized Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) for Cyber Intrusion Protection
Telecom networks are susceptible to a wide range of cyber threats, including insider threats, ransomware, Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, and advanced malware like GTPDOOR. The constantly changing landscape of cybersecurity presents significant challenges for Security Operations teams, making it difficult to detect anomalies, respond in real time, and protect critical telecom infrastructure.
In addition, telecom network elements have unique performance requirements, including high availability, low latency, and ease of maintenance, especially for core networks. EDR solutions must avoid resource competition with these elements and quickly adapt to hardware and software changes. They must also comply with regulatory standards such as the EU's NIS2 directive and the U.S. Transportation Security Administration (TSA) requirements, while adhering to 3GPP protocol specifications.
To effectively safeguard these network elements, a telecom-specific approach is required—one that eliminates blind spots and enables real-time detection and response to threats, without affecting network function performance or integrity.
Enhancing Cyber Intrusion Detection with Network Detection and Response (NDR)
Many telecom operators are combining Network Detection and Response (NDR) with EDR solutions to counteract evolving network and endpoint threats. By consolidating data from network elements and traffic, operators gain enhanced visibility across the network layer. This integration accelerates threat detection, providing more precise insights into malicious activities, even in areas where agentless network functions or sophisticated EDR evasion tactics might create blind spots.
Modern technologies are merging EDR and NDR capabilities into a single unified view, offering real-time threat detection and visibility across network functions, data, and traffic. This synergy effectively eliminates blind spots, ensuring comprehensive protection.
Achieving Comprehensive Cyber Protection for Telecom Networks
Telecommunications networks do more than provide connectivity—they serve as the foundation of critical infrastructure, supporting services that require global resilience against disruptions. Advanced threats, such as GTPDOOR, underscore the urgent need for strong cybersecurity measures. Communications Service Providers (CSPs) are advised to invest in solutions designed for multi-vendor telecom networks to strengthen their defenses against these evolving cyber threats.
Source: NETWORK Computing
Cite this article:
Priyadharshini S (2024), "Strengthening Telecom Networks Against Cybersecurity Threats", AnaTechMaz, pp. 134