Artificial Intelligence
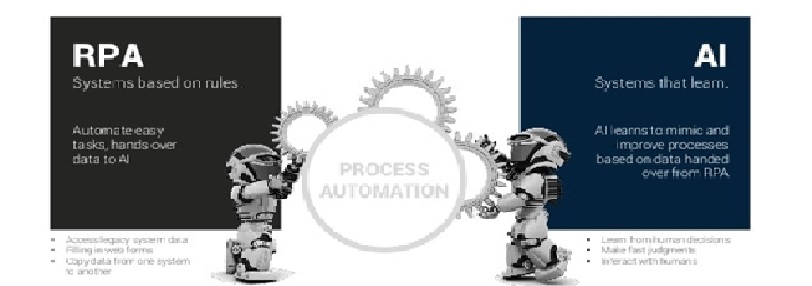
Artificial intelligence (AI) makes it possible for machines to learn from experience, adjust to new inputs and perform human-like tasks. Most AI examples that you hear about today – from chess-playing computers to self-driving cars – rely heavily on deep learning and natural language processing as shown in figure 1. Using these technologies, computers can be trained to accomplish specific tasks by processing large amounts of data and recognizing patterns in the data.
Artificial intelligence (AI), the ability of a digital computer or computer-controlled robot to perform tasks commonly associated with intelligent beings. The term is frequently applied to the project of developing systems endowed with the intellectual processes characteristic of humans, such as the ability to reason, discover meaning, generalize, or learn from past experience. Since the development of the digital computer in the 1940s, [1] it has been demonstrated that computers can be programmed to carry out very complex tasks—as, for example, discovering proofs for mathematical theorems or playing chess—with great proficiency. Still, despite continuing advances in computer processing speed and memory capacity, there are as yet no programs that can match human flexibility over wider domains or in tasks requiring much everyday knowledge. On the other hand, some programs have attained the performance levels of human experts and professionals in performing certain specific tasks, so that artificial intelligence in this limited sense is found in applications as diverse as medical diagnosis, computer search engines, and voice or handwriting recognition.
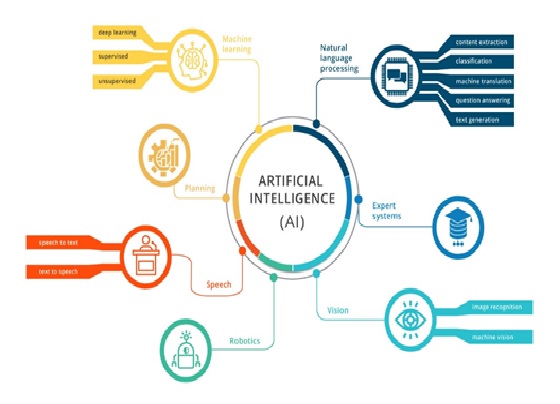
Figure 1: Artificial Intelligence
Importance of Artificial Intelligence
- AI automates repetitive learning and discovery through data. Instead of automating manual tasks, AI performs frequent, high-volume, computerized tasks. [2] And it does so reliably and without fatigue. Of course, humans are still essential to set up the system and ask the right questions.
- AI adds intelligence to existing products. Many products you already use will be improved with AI capabilities, much like Siri was added as a feature to a new generation of Apple products. Automation, conversational platforms, bots and smart machines can be combined with large amounts of data to improve many technologies. Upgrades at home and in the workplace, range from security intelligence and smart cams to investment analysis.
- AI adapts through progressive learning algorithms to let the data do the programming. AI finds structure and regularities in data so that algorithms can acquire skills.[3] Just as an algorithm can teach itself to play chess, it can teach itself what product to recommend next online. And the models adapt when given new data.
- AI achieves incredible accuracy through deep neural networks. For example, your interactions with Alexa and Google are all based on deep learning. And these products keep getting more accurate the more you use them. In the medical field, AI techniques from deep learning and object recognition can now be used to pinpoint cancer on medical images with improved accuracy.
- AI gets the most out of data. When algorithms are self-learning, the data itself is an asset. The answers are in the data. You just have to apply AI to find them. Since the role of the data is now more important than ever, it can create a competitive advantage. If you have the best data in a competitive industry, even if everyone is applying similar techniques, the best data will win.
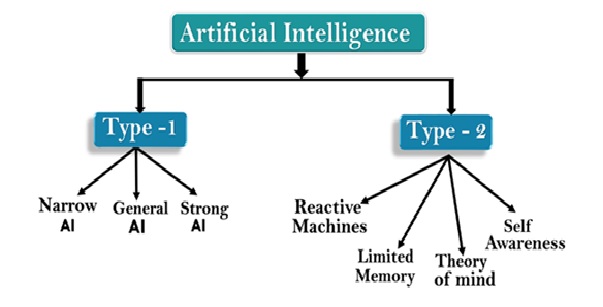
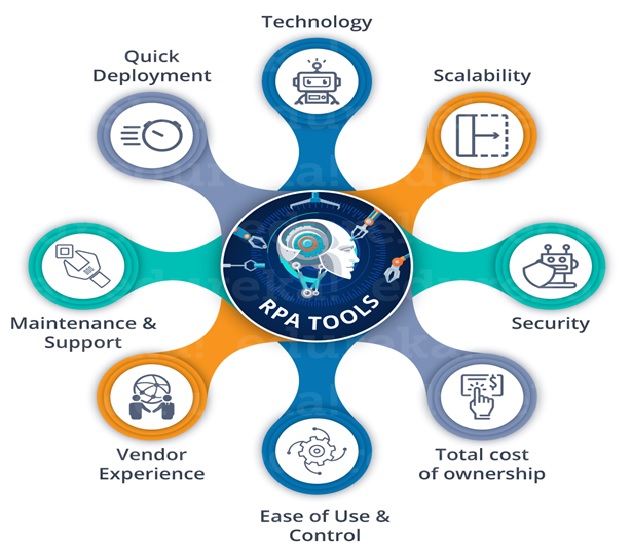
Every industry has a high demand for AI capabilities – including systems that can be used for automation, learning, legal assistance, [4] risk notification and research as shown in figure 2. Specific uses of AI in industry include:
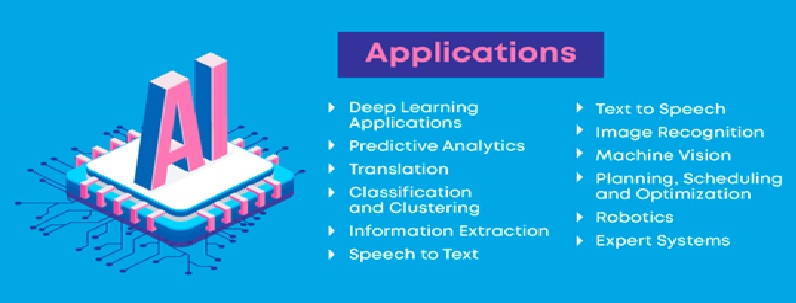
Figure 2: Applications of Artificial Intelligence in business
- Machine learning automates analytical model building. It uses methods from neural networks, statistics, operations research and physics to find hidden insights in data without explicitly being programmed for where to look or what to conclude.
- A neural network is a type of machine learning that is made up of interconnected units (like neurons) that processes information by responding to external inputs, relaying information between each unit. The process requires multiple passes at the data to find connections and derive meaning from undefined data.
- Deep learning uses huge neural networks with many layers of processing units, taking advantage of advances in computing power and improved training techniques to learn complex patterns in large amounts of data. Common applications include image and speech recognition.
- Computer vision relies on pattern recognition and deep learning to recognize what’s in a picture or video. When machines can process, analyze and understand images, they can capture images or videos in real time and interpret their surroundings.
- Natural language processing (NLP) is the ability of computers to analyze, understand and generate human language, including speech. The next stage of NLP is natural language interaction, which allows humans to communicate with computers using normal, everyday language to perform tasks.
Purpose of Artificial Intelligence
The purpose of Artificial Intelligence is to aid human capabilities and help us make advanced decisions with far-reaching consequences. [5] That’s the answer from a technical standpoint. From a philosophical perspective, Artificial Intelligence has the potential to help humans live more meaningful lives devoid of hard labour, and help manage the complex web of interconnected individuals, companies, states and nations to function in a manner that’s beneficial to all of humanity. Currently, the purpose of Artificial Intelligence is shared by all the different tools and techniques that we’ve invented over the past thousand years – to simplify human effort, and to help us make better decisions. Artificial Intelligence has also been touted as our Final Invention, a creation that would invent ground-breaking tools and services that would exponentially change how we lead our lives, by hopefully removing strife, inequality and human suffering.
Advantages of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Reduction in human error
- Available 24×7
- Helps in repetitive work
- Digital assistance
- Faster decisions
- Rational Decision Maker
- Medical applications
- Improves Security
- Efficient Communication
References:
- https://www.sas.com/en_us/insights/analytics/what-is-artificial-intelligence.html
- https://www.britannica.com/technology/artificial-intelligence
- https://www.brookings.edu/research/what-is-artificial-intelligence/
- https://www.mygreatlearning.com/blog/what-is-artificial-intelligence/
- https://www.europarl.europa.eu/news/en/headlines/society/20200827STO85804/what-is-artificial-intelligence-and-how-is-it-used
Cite this article:
D. Vinotha (2021), Artificial Intelligence, AnaTechMaz, pp. 3