Graphene Materials
Graphene represents a conceptually new class of materials that are only one atom thick, so-called two-dimensional (2D) materials (they are called 2D because they extend in only two dimensions: length and width; as the material [1] is only one atom thick, the third dimension, height, is considered to be zero).
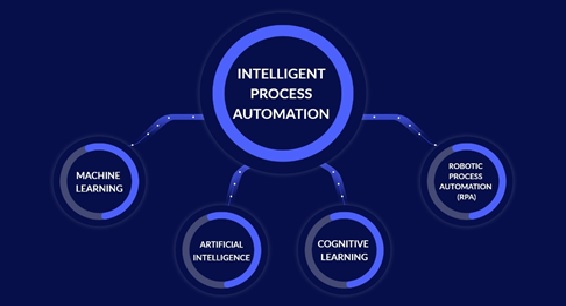
Graphene's properties
Graphene is the thinnest material known to man at one atom thick, and also incredibly strong - about 200 times stronger than steel. On top of that, graphene is an excellent conductor of heat and electricity and has interesting light absorption abilities. It is truly a material that could change the world, with unlimited potential for integration in almost any industry.
Several companies offer graphene and graphene based products. You may check our list of graphene related companies to find a [2] company that offers the products you need.
In December 2011 Vorbeck Materials said that the Siren anti-theft packaging device, which uses their graphene-based Vor-Ink circuitry (shown below) has started shipping - and this was the world's first commercially available product that is based on graphene.
An interesting market for graphene is the sensors market. In 2016 for example San Diego-based Nanomedical Diagnostics (now called Cardea) started shipping its graphene-based sensors and the AGILE R100 [3] system which allows for real-time detection of small molecules. The graphene sensor offers faster sample processing, greater accuracy, portability and cost savings the figure1 shown given below.

Figure1: Graphene Materials.
Graphene Properties
This wonder nanomaterial has the following properties:
- 200 times stronger than steel, yet incredibly lightweight, due to the compact structure and the strong covalent bonding between the carbon atoms.
- Ultra-light yet immensely tough.
- Flexible and can be bent or folded.
- Can act as a perfect barrier due to its compact structure. Not even helium can pass through it.
- Transparent due to its infinitesimal thickness. Graphene absorbs only 2.3% of light transmitted [4] through it so that it is almost invisible.
- The thinnest material known to exist.
- Chemically inert.
Nontoxic
- Because the fourth electron, the pi (π) electron, from the carbon atom's valence shell is not naturally raised to a higher level there is no band gap associated with a separate conduction band.
- Electrically and thermally conductive with better conductivity than copper due to the highly mobile free pi (π) electrons.
- Since carbon [5] is the Earth's fourth most common element, graphene is very inexpensive.
- Stretchable causing a change in sheet resistance. Can be stretched by as much as 20 per cent without inducing defects.
References:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graphene
- https://www.nanowerk.com/what_is_graphene.php
- https://www.graphene-info.com/graphene-applications
- www.nanowerk.com/what_is_graphene.php
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graphene
Cite this article:
S. Nandhinidwaraka (2021), Graphene Material, AnaTechMaz, pp. 10