Smaller, Cheaper Lidar with New Chip-Based Beam Steering Device
Researchers have developed a new chip-based beam steering technology that provides a promising route to small, cost-effective, and high-performance lidar systems. Lidar, or light detection and ranging, uses laser pulses to acquire 3D information about a scene or object. It is used in a wide range of applications such as autonomous driving, 3D holography, biomedical sensing, free-space optical communications, and virtual reality.
“Although devices known as chip-based optical phased arrays (OPAs) can quickly and precisely steer light in a non-mechanical way, so far, these devices have had poor beam quality and a field of view typically below 100 degrees.” [1]
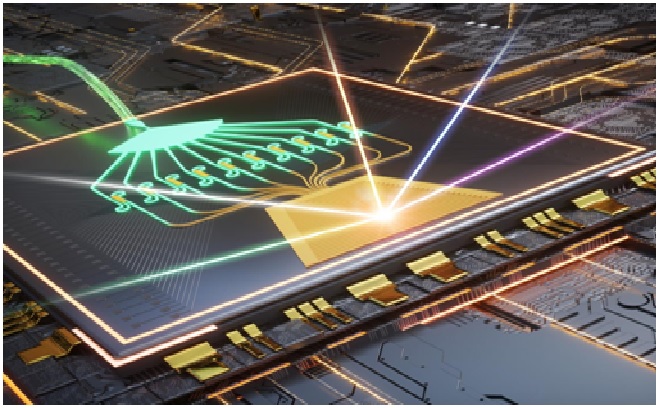
Figure 1. Smaller, Cheaper Lidar with New Chip-Based Beam Steering Device
Figure 1 shows “We believe that our results are groundbreaking in the field of optical beam steering,” Hu said. “This development lays the foundation for a low-cost and compact OPA-based lidar that will allow lidar to be widely used for a variety of applications, such as advanced high-level driver assistance systems that can help with driving and parking and increase safety.” [2]
A new OPA design
OPAs perform beam steering by electronically controlling light's phase profile to form specific light patterns. Most OPAs use an array of waveguides to emit many beams of light and then interference is applied in far field (away from the emitter) to form the pattern. However, the fact that these waveguide emitters are typically spaced far apart from each other and generate multiple beams in the far field creates an optical artifact known as aliasing. The researchers also applied additional optical techniques to lower the background noise and reduce other optical artifacts such as side lobes. [3]
High quality and wide field of view
To test their new device, the scientists built a special imaging system to measure the average optical power in the far field along the horizontal direction over a 180° field of view. They demonstrated aliasing-free beam steering in this direction, including steering beyond ±70°, although some beam degradation was observed.
They then characterized beam steering in the vertical direction by tuning the wavelength from 1480 nm to 1580 nm, achieving a tuning range of 13.5°. Finally, they demonstrated the versatility of the OPA by using it to create 2D images of the letters “D”, “T” and “U” centered at the angles of -60°, 0° and 60° by they tuned both the wavelength and the phase shifters. [4]
References:
- https://scitechdaily.com/smaller-cheaper-lidar-with-new-chip-based-beam-steering-device/
- https://journalbreak.com/smaller-cheaper-lidar-with-new-chip-based-beam-steering-device/
- https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2022/08/220804102624.htm
- https://techsens.in/smaller-cheaper-lidar-with-new-chip-based-beam-steering-device/
Cite this article:
Thanusri swetha J (2022), Smaller, Cheaper Lidar with New Chip-Based Beam Steering Device, AnaTechMaz, pp.155