Self-Services BI Interfaces
Self-service BI is a trend with a somewhat vague definition. In the most general sense, self-service BI tasks are those that business users carry out themselves instead of passing them on to IT for fulfillment. The aim is to give the users of BI tools more freedom and responsibility at the same time. At its heart lies the notion of user independence and self-sufficiency when it comes to the use of corporate information, which leads to a decentralization of BI in the organization.[1]
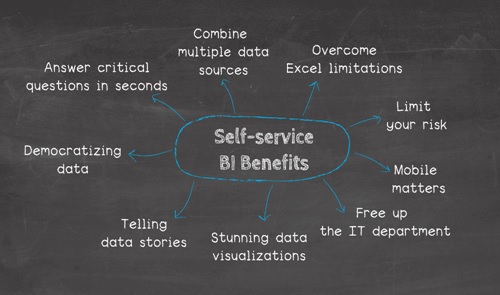
Figure 1. the self services BI Interfaces
Figure 1 shows The expanded data access and analytics capabilities that self-service BI provides can benefit businesses in a variety of ways. The potential benefits include:
- Better use of BI and IT resources. Because business users can do their own ad hoc analysis, self-service BI frees an organization's BI and IT teams from creating the majority of queries, visualizations, dashboards and reports. That allows them to focus on higher-value priorities and tasks that require more technical skills, such as curating data sets for business users and creating complex queries.
- Faster data analysis and decision-making. Self-service capabilities help reduce bottlenecks in BI programs by shifting analytics work to business users instead of a small number of BI professionals. That in turn accelerates business processes, because users can more quickly analyze data and then make decisions and take actions.
- A data-driven organization. As more business executives, managers and workers use BI tools, self-service systems can help create a fully data-driven culture in both the C-suite and business operations.
- Competitive advantages. The expanded use of data and accelerated decision-making can make an organization more agile as a whole, which may help it create or maintain a competitive edge in the marketplace -- particularly if its use of self-service tools is more substantial and successful than similar efforts by business rivals.[2]
Self-service BI vs. Corporate BI
Enterprise BI (or “corporate BI”) is the widespread deployment of BI platforms and processes throughout an enterprise business or corporation. Corporate BI includes deploying data warehouses, new databases, data-mapping projects, and more depending on the enterprise’s needs. The goals of enterprise BI and SSBI are similar:
- Empower users to use data for decision-making
- Prioritize clean, timely, and relevant data for analysis
- Share data insights across teams and executive leadership
However, enterprise BI often involves an entire overhaul of how data is ingested and used in the organization. Usually, the self-service aspect focuses on analytics and reporting processes and how project owners delegate those processes to business teams of all technical abilities. SSBI doesn’t necessarily need an organization-wide deployment, but corporate BI and SSBI aren’t mutually exclusive either. Many of our customers have deployed SSBI across their entire enterprise.[3]
Self-service business intelligence (SSBI) empowers teams such as product developers, sales, finance, marketing, operations, and more to answer data questions, with governance supported by IT and business intelligence (BI) analysts. BI is the strategic process of using data insights to make decisions that help organizations reach their goals. Instead of using gut instinct, precedents, and traditional mindsets, self-service BI helps to create a new culture around using data every day.[3]
References:
- https://bi-survey.com/self-service-bi
- https://searchbusinessanalytics.techtarget.com/definition/self-service-business-intelligence-BI
- https://www.tableau.com/learn/articles/business-intelligence/self-service-bi
Cite this article:
Thanusri swetha J (2021), Self Services BI Interfaces, AnaTechMaz, pp. 26