The Technology of 4D Printing in a new Dimension
4D printing is the process through which a 3D printed object transforms itself into another structure over the influence of external energy input as temperature, [1] light or other environmental stimuli. The 4D printing new dimension process is shown in figure 1.
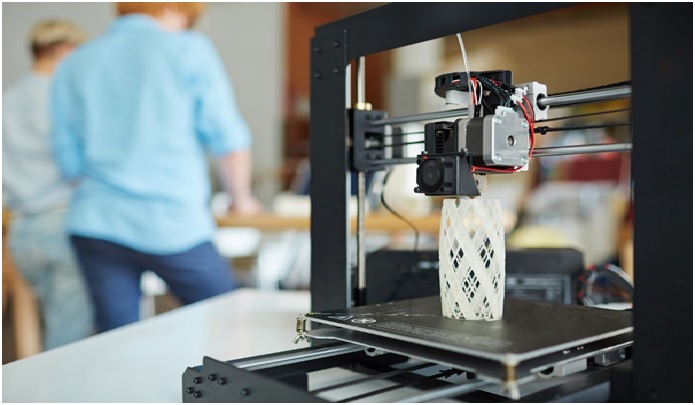

Figure 1.The 4D Printing
Figure 1 This technology is part of the project of MIT Self-assembly Lab. The purpose of this project is to combine technology and design to invent self-assembly and programmable material technologies aiming at reimagining construction, manufacturing, product assembly, and performance.
Obviously, 4D Printing has one more “D” than 3D Printing. 3D Printing is about repeating a 2D structure, layer by layer in a print path, from the bottom to the top, layer by layer until a 3D volume is created. 4D Printing is referred to as 3D printing transforming over time. Thus, a fourth dimension is added: time. So, the big breakthrough about 4D Printing over 3D Printing technology is its ability to change shape over time.
Getting to grips with 4D printing first requires an understanding of how a material will react to a certain stimulus. Using this knowledge of material behaviour, [3] engineers can design an object with variations in its material structure.
Based on digital CAD design, a model is then 3D printed, either in a single or in a composite material. Once the printing process is complete, a pre-programmed geometric code will dictate how different areas of the object should react to a specific stimulus.
However, 4D printing adds a new dimension, where the structure can change its shape over time. It requires unique materials and customized designs to be built into the program to prompt the 3D print to change shape when triggered by a specific stimulus, such as heat, water or light.
This programmable ingredient a hydrogel or shape memory polymer [4] is capable of altering its physical shape or thermomechanical properties in a programmable way based on user input or autonomous sensing. Hydrogels can absorb large amounts of water and can be programmed to shrink or expand with changes in the external environment. Shape memory polymers can return to their original shape from a deformed one when a stimulus is applied.
Several research and development projects specific to 4D printing are underway in industries, such as healthcare, electronics, automotive, aerospace and defence, consumer appliances (fashion and consumer durables), textile, construction, and industrial machinery. Despite being a novel technology, [5] potential opportunities presented by 4D printing are vast and are acknowledged by several experts in the field.
The market for 4D printing is beginning to establish, owing to numerous research and development activities. The opinion of market growth is varied among experts. The optimistic view of the technology suggests that the market would grow at a CAGR of approximately 33% (an estimated increase in market size from US$35 million in 2019 to US$200 million by 2025). However, being a novel technology in its infancy stages, Future Bridge predicts that the 4D printing market would grow at a slightly slower rate of 20% by 2025
References:
- https://www.sculpteo.com/en/3d-learning-hub/best-articles-about-3d-printing/4d-printing-technology/
- https://emag.medicalexpo.com/lets-4d-printing-in-a-new-dimension/
- https://amfg.ai/2019/02/05/what-is-4d-printing/
- https://www.azom.com/article.aspx?ArticleID=19378
- https://www.futurebridge.com/industry/perspectives-mobility/4d-printing-the-technology-of-the-future/
Cite this article:
Vinotha D (2022), The Technology of 4D Printing in a new Dimension, AnaTechMaz, pp.125