The Technology Development of Smart Grid
A smart grid is an electricity network based on digital technology that is used to supply electricity to consumers via two-way digital communication. This system allows for monitoring, analysis, control and communication within the supply chain to help improve efficiency, reduce energy consumption and cost, and maximize the transparency and reliability of the energy supply chain. [1] The smart grid was introduced with the aim of overcoming the weaknesses of conventional electrical grids by using smart net meters.
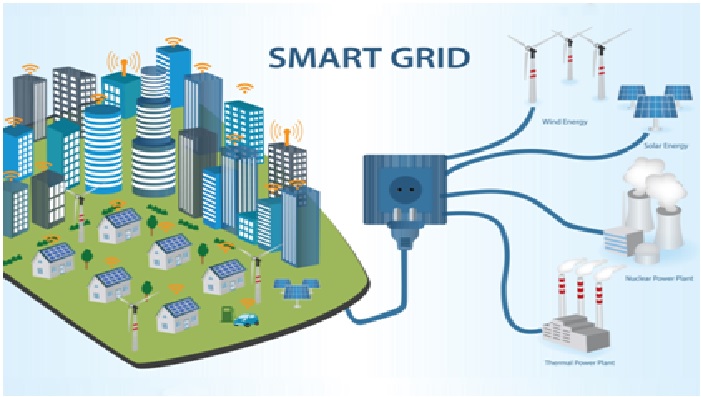
Figure 1. The Smart Grid [2]
Many government institutions around the world have been encouraging the use of smart grids for their potential to control and deal with global warming, emergency resilience and energy independence scenarios. The smart grid is shown in figure 1.
A modern smart grid system has the following capabilities:
- It can repair itself.
- It encourages consumer participation in grid operations.
- It ensures a consistent and premium-quality power supply that resists power leakages.
- It allows the electricity markets to grow and make business.
- It can be operated more efficiently.
Big data analytics and IoT technologies are important technology drivers in smart grids whereby analytics shift to the edge, as in edge computing. [3] Smart grids leverage more technologies but aren’t just about IT nor even technologies. A smart grid serves several purposes and the movement from traditional electric grids to smart grids is driven by multiple factors.
These include the deregulation of the energy market, evolutions in metering, changes on the level of electricity production, decentralization (distributed energy), the advent of the involved ‘prosumer’, changing regulations, the rise of microgeneration and (isolated) microgrids, renewable energy mandates with more energy sources and new points where and purposes for which electricity is needed (e.g. electrical vehicle charging points).
An electrical grid or electric grid is a network to deliver electricity from the producer(s) and places where it’s generated and transformed (power plants and substations) to the final destinations where electricity is ‘consumed’: households, businesses, various facilities and the consumer in general. In practice it is a highly interconnected network with several components such as substations, transmission lines and wiring, distribution lines, transformers and more.
“Smart grid” technologies are made possible by two-way communication technologies, control systems, and computer processing. These advanced technologies include advanced sensors known as Phasor Measurement Units (PMUs) that allow operators to assess grid stability, [4] advanced digital meters that give consumers better information and automatically report outages, relays that sense and recover from faults in the substation automatically, automated feeder switches that re-route power around problems, and batteries that store excess energy and make it available later to the grid to meet customer demand.
This exciting transformation of the nation’s electric grid creates both challenges and opportunities to advance the capabilities of today’s electricity delivery system. A critical component of grid modernization is a coordinated, strategic research, development and demonstration (RD&D) effort that involves both the public and private sectors.
References:
- https://www.techopedia.com/definition/692/smart-grid
- https://innovationatwork.ieee.org/smart-grid-transforming-renewable-energy/
- https://www.i-scoop.eu/industry-4-0/smart-grids-electrical-grid/
- https://www.energy.gov/oe/activities/technology-development/grid-modernization-and-smart-grid
Cite this article:
Vinotha D (2022), The Technology Development of Smart Grid, AnaTechMaz, pp.108