Overview of OpenRAN Reference Architecture
Open RAN is a collaboration of equipment makers and telecoms in various working groups to solve this interoperability problem by creating standards. As long as equipment meets open RAN standards it should be compatible with gear made by any other vendor whose gear also meets the standards. Without having to rely on one vendor for all the equipment, carriers and enterprises have more opportunity to shop around for the best deal on each piece.
Open RAN standards would also be available to software developers that could readily write innovative features and services to respond quickly to user’s needs. [1]
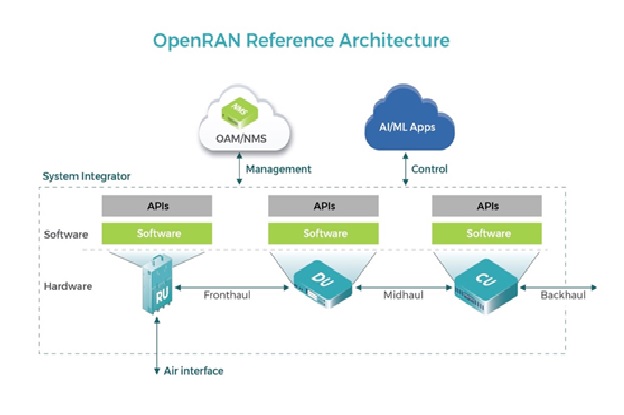
Figure 1. The Overview of OpenRAN Reference Architecture
Figure 1 shows 5G radio, or NR (New Radio), improves spectral efficiency and delivers unprecedented network capacity. 5G New Radio technology is based on flexible OFDM waveforms and multiple access techniques, optimized for various 5G services, applications, and deployment use cases. 5G (NR) features are defined by various 3GPP standards, with first phase completion in Rel-15 and second phase in Rel-16. [3]
The O-RAN Architecture
The O-RAN architecture is well documented in the O-RAN alliance. The key elements of O-RAN architecture are:
- Service Management and Orchestration Framework (SMO) – includes an integration fabric and data services for the functions it manages. It allows managed functions to interoperate and communicate within the O-RAN. The SMO connects to and manages the RICs, O-Cloud, the O-CU, and O-DU.
- RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) – There are two types of RICs – non-real-time and near-real-time. Both are logical functions for controlling and optimizing the elements and resources of an O-RAN. A near-real-time RIC controls and optimizes elements and resources with granular data collection and communication over the E2 interface. The E2 interface connects the near-real-time RIC with the O-CU and O-DU
- O-Cloud – a cloud computing platform made up of the physical infrastructure nodes using O-RAN architecture. It also creates and hosts the various virtual network functions (VNFs) used by the RICs and other infrastructure elements.
- O-RAN central unit (O-CU) – Logical node that hosts a handful of protocols, which are the radio resource control (RRC), service data adaptation protocol (SDAP), and packet data convergence protocol (PDCP).
- O-RAN distributed unit (O-DU) – Logical node that hosts another set of protocols, which are the radio link control (RLC) protocol, medium access control (MAC) protocol, and the physical interface (PHY).
- O-RAN Radio unit (O-RU) – It processes radio frequencies received by the physical layer of the network. The processed radio frequencies are sent to the O-DU through a front haul interface. [2]
References:
- https://www.networkworld.com/article/3632859/what-is-open-ran.html
- https://www.stl.tech/blog/understanding-o-ran-from-the-basics/
- https://www.parallelwireless.com/products/5g-openran/
Cite this article:
Thanusri swetha J (2021), Overview of OpenRAN Reference Architecture, Anatechmaz, pp. 57