The Components of Data Fabrics
A data fabric is an architecture and set of data services that provide consistent capabilities across a choice of endpoints spanning hybrid multicloud environments. It is a powerful architecture that standardizes data management practices and practicalities across cloud, on premises, and edge devices. Among the many advantages that a data fabric affords, data visibility and insights, data access and control, data protection, and security quickly rise to the top.[1]
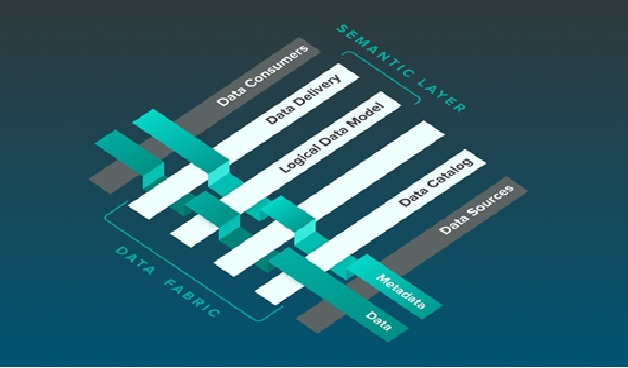
Figure 1. the Components of Data Fabrics
Figure 1 shows Data fabric is an end-to-end data integration and management solution, consisting of architecture, data management and integration software, and shared data that helps organizations manage their data. A data fabric provides a unified, consistent user experience and access to data for any member of an organization worldwide and in real-time.
Data fabric is designed to help organizations solve complex data problems and use cases by managing their data—regardless of the various kinds of applications, platforms, and locations where the data is stored. Data fabric enables frictionless access and data sharing in a distributed data environment.[3]
6 Components of Data Fabric
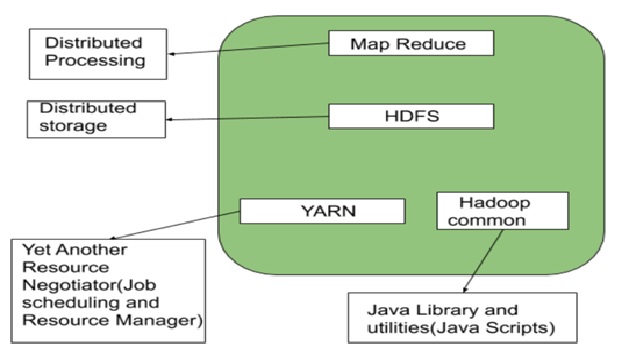
Data Ingestion
It needs to work with all potential data formats, both structured and unstructured, from various sources, including data streams, applications, cloud sources, and databases. Also, it must support batch, real-time, and stream processing.
Data Processing
It provides you with a set of tools to help you curate and transform your data to make it analytics-ready to be used by downstream BI tools.
Data Management and Intelligence
It allows you to secure your data and enforce governance by determining who can see what data. This is also where you can apply global structures such as Metadata Management, search, and lineage control.
Data Orchestration
This component coordinates the operation of all stages throughout the end-to-end data workflow. It lets you define when and how often you should run the pipelines and how you can manage the data produced by those pipelines.
Data Discovery
You can employ data modeling, data preparation, and data curation in this layer. It allows your analysts to find and consume the data across two “silos” as if they were part of the same dataset and extract valuable insights from it. This is probably the most important part of the data fabric as it focuses on solving the silo problem.
Data Access
It delivers your data to analysts directly or through queries, APIs, data services, and dashboards.
This layer often builds semantics, intelligence, and rules into data access mechanisms to provide the data in the required form and format.[2]
References:
- https://www.netapp.com/data-fabric/what-is-data-fabric/
- https://scalefresh.com/understanding-data-fabric-6-main-components-what-they-do/
- https://www.tibco.com/reference-center/what-is-data-fabric
Cite this article:
Thanusri swetha J (2021), The Components of Data Fabrics ,AnaTechMaz, pp. 34