Biopower: Renewable Electricity Generation Technologies
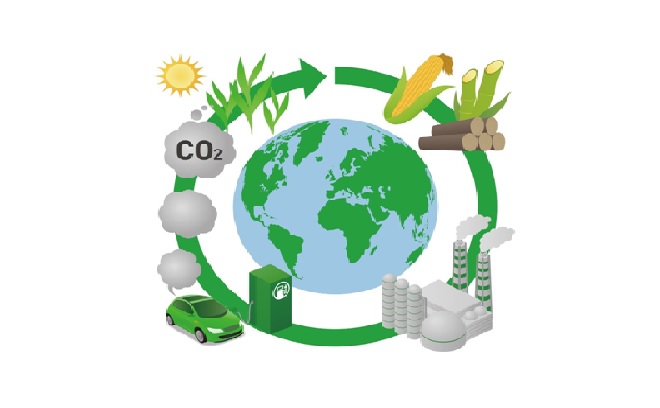
Biopower technologies convert renewable biomass fuels into heat and electricity using processes similar to those used with fossil fuels. [1] There are three ways to release the energy stored in biomass to produce biopower: burning, bacterial decay, and conversion to gas/liquid fuel. Figure 1 shows the biopower process.
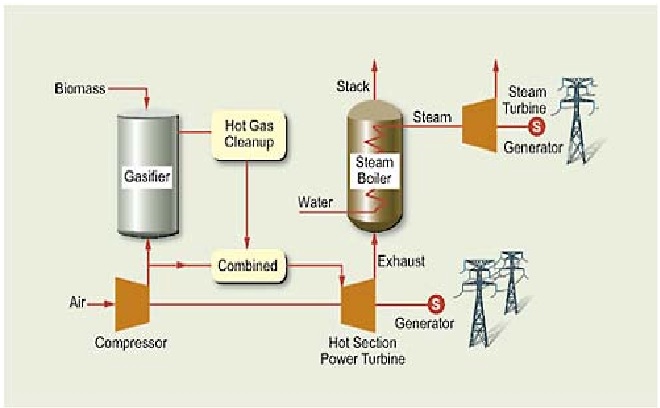
Figure 1: The Biopower Electricity Technologies [2]
Most electricity generated from biomass is produced by direct combustion. Biomass is burned in a boiler to produce high-pressure steam. This steam flows over a series of turbine blades, causing them to rotate. The rotation of the turbine drives a generator, producing electricity. Biomass can also serve as substitute for a portion of coal in an existing power plant furnace in a process called co-firing (combusting two different types of materials at the same time).
Organic waste material, such as animal dung or human sewage, is collected in oxygen-free tanks called digesters. Here, the material is decomposed by anaerobic bacteria that produce methane and other by products to form a renewable natural gas, which can then be purified and used to generate electricity.
We're making cost-effective investments in biopower within our retail states while complying with renewable [3] energy mandates.
- Testing the co-firing of wood with fossil fuel at select existing facilities while exploring the possibility of retrofitting units that will generate electricity by burning wood fuel only.
- Supplying customers with power from Landfill Methane Projects.
- Planning to procure electricity derived from biomass, animal waste and municipal solid waste as stipulated in the state’s Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency Portfolio Standard.
- Partnering with local research organizations to develop new technologies.
The decay of biomass produces a gas – methane – that can be used as an energy source. In landfills, wells can be drilled to release the methane from the decaying organic matter. Then pipes from each well carry the gas to a central point where it is filtered and cleaned before burning. Methane also can be produced from biomass through a process called anaerobic digestion. [4] Anaerobic digestion involves using bacteria to decompose organic matter in the absence of oxygen.
Methane can be used as an energy source in many ways. Most facilities burn it in a boiler to produce steam for electricity generation or for industrial processes. Two new ways include the use of microturbines and fuel cells. Microturbines have outputs of 25 to 500 kilowatts. About the size of a refrigerator, they can be used where there are space limitations for power production. Methane can also be used as the “fuel” in a fuel cell. Fuel cells work much like batteries but never need recharging, producing electricity as long as there’s fuel.
Generating heat and power from waste aside, the major issue for ‘green’ power is ironically the same as for ‘green’ fuels – sustainability. That is particularly true for the wood that is being used as a feedstock. [5] The cost of transporting wood has made biopower most economic on a small scale.
This is where the main benefits come, too, providing local employment and feeding cash into the local economy. The trend now, though, is towards industrial-scale installations. Greenpeace has already warned that forests in Canada are being cut down (‘whole-tree harvesting’) to feed these large-scale installations at home and abroad.
References:
- https://www.energy.gov/eere/bioenergy/biopower
- https://nap.nationalacademies.org/read/12619/chapter/5
- https://www.duke-energy.com/our-company/environment/renewable-energy/biopower
- https://www.renewableenergyworld.com/types-of-renewable-energy/tech/biopower/#gref
- https://www.power-technology.com/analysis/featurebanking-on-biopower/
Cite this article:
Vinotha D (2022), Biopower: Renewable Electricity Generation Technologies, AnaTechMaz, pp.54