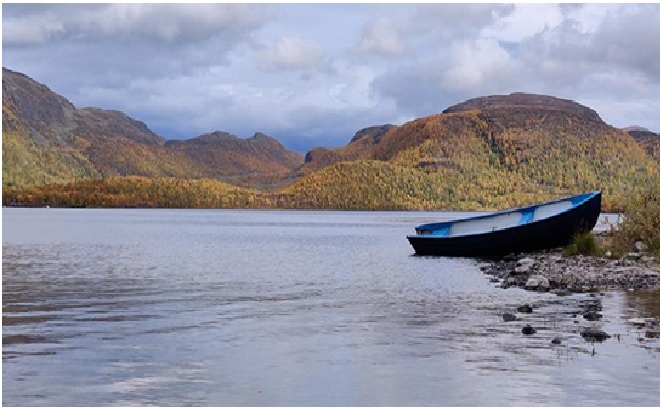
Biomass: A Renewable Energy Resource
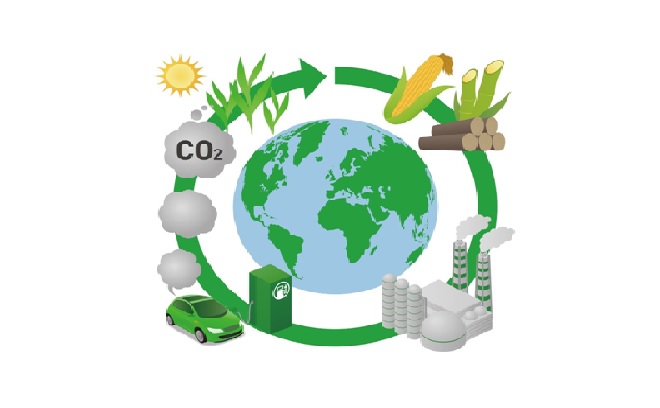
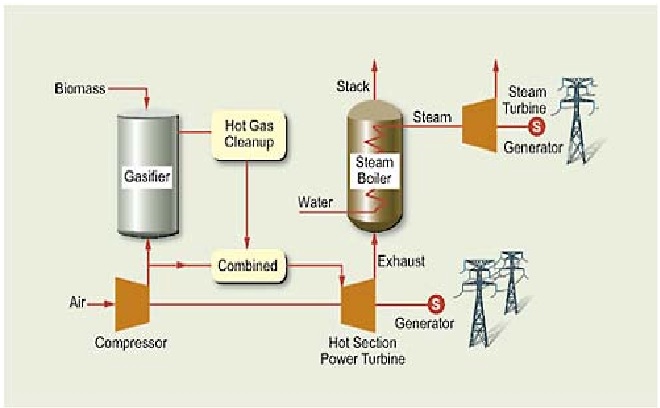
Biomass power is electricity generated from renewable organic waste that would otherwise be dumped in landfills, openly burned, or left in the woods as fodder for forest fires. [1] The figure 1 shows the biomass energy.

Figure 1: The Biomass Energy [2]
In biomass power plants, wood waste or other waste is burned to produce steam that runs a turbine to make electricity, or that provides heat to industries and homes. Fortunately, new technologies — including pollution controls and combustion engineering — have advanced to the point that any emissions from burning biomass in industrial facilities are less than emissions produced when using fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, oil). ReEnergy’s facilities use this state-of-the- art technology.
Biomass power provides significant environmental and consumer benefits, including improving forest health and forest air quality, and offering baseload, dependable electricity to complement intermittent sources of electricity.
Biomass can be burned by thermal conversion and used for energy. Thermal conversion involves heating the biomass feedstock in order to burn, dehydrate, or stabilize it. [3] The most familiar biomass feedstocks for thermal conversion are raw materials such as municipal solid waste (MSW) and scraps from paper or lumber mills.
Different types of energy are created through direct firing, co-firing, pyrolysis, gasification, and anaerobic decomposition.
Before biomass can be burned, however, it must be dried. This chemical process is called torrefaction. During torrefaction, biomass is heated to about 200° to 320° Celsius (390° to 610° Fahrenheit). The biomass dries out so completely that it loses the ability to absorb moisture, or rot. It loses about 20% of its original mass, but retains 90% of its energy. The lost energy and mass can be used to fuel the torrefaction process.
- Pyrolysis entails heating organic materials to 800–900oF (400–500 oC) in the near complete absence of free oxygen. [4] Biomass pyrolysis produces fuels such as charcoal, bio-oil, renewable diesel, methane, and hydrogen.
- Hydrotreating is used to process bio-oil (produced by fast pyrolysis) with hydrogen under elevated temperatures and pressures in the presence of a catalyst to produce renewable diesel, renewable gasoline, and renewable jet fuel.
- Gasification entails heating organic materials to 1,400–1700oF (800–900oC) with injections of controlled amounts of free oxygen and/or steam into the vessel to produce a carbon monoxide and hydrogen rich gas called synthesis gas or syngas. Syngas can be used as a fuel for diesel engines, for heating, and for generating electricity in gas turbines. It can also be treated to separate the hydrogen from the gas, and the hydrogen can be burned or used in fuel cells.
References:
- https://reenergyholdings.com/renewable-energy/what-is-biomass/
- https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/biomass-energy
- https://www.istockphoto.com/photos/biomass
- https://www.eia.gov/energyexplained/biomass/
Cite this article:
Vinotha D (2022), Biomass: A Renewable Energy Resource, AnaTechMaz, pp.53