Brain-Machine Interfaces (BMIs)
Brain-machine interfaces (BMIs) are a type of technology that enables direct communication between the brain and an external device, such as a computer or prosthetic limb. BMIs use various methods to interpret neural signals from the brain and translate them into control signals for the external device, allowing users to interact with the device using their thoughts.
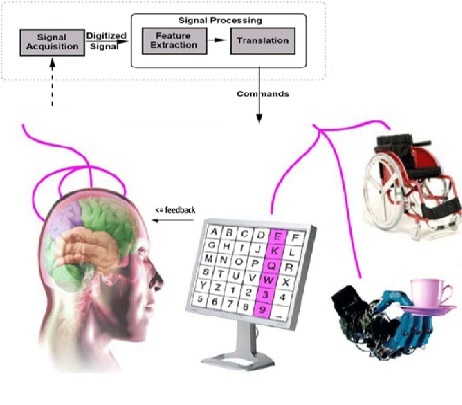
Figure 1. Brain-Machine Interfaces. [1]
Figure 1 shows Brain-machine interfaces. There are several types of BMIs, including invasive, partially invasive, and non-invasive. Invasive BMIs involve the implantation of electrodes or other devices directly into the brain tissue, allowing for highly precise and detailed neural recordings. Partially invasive BMIs use electrodes implanted on the surface of the brain or in the skull, while non-invasive BMIs use external sensors, such as electroencephalography (EEG) or functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), to measure neural activity through the scalp.
BMIs have many potential applications in the medical field, including the development of prosthetic limbs that can be controlled directly by the user's thoughts, the restoration of mobility and communication for individuals with paralysis or neurological disorders, and the treatment of chronic pain and other conditions. BMIs also have potential applications in research, such as studying the neural basis of perception, cognition, and behavior.
Despite the promising potential of BMIs, there are still many challenges to be overcome in their development and implementation. These challenges include the development of more reliable and robust neural signal decoding algorithms, the improvement of implant longevity and safety, and the mitigation of ethical and societal concerns regarding the use of invasive BMIs. Nonetheless, research in this area is ongoing, and the continued advancement of BMIs has the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with technology and with each other.
References:
- https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Brain-Machine-Interface-BMI-concept_fig2_336222389
Cite this article:
Hana M (2023), Brain-Machine Interfaces, AnaTechMaz ,pp.143