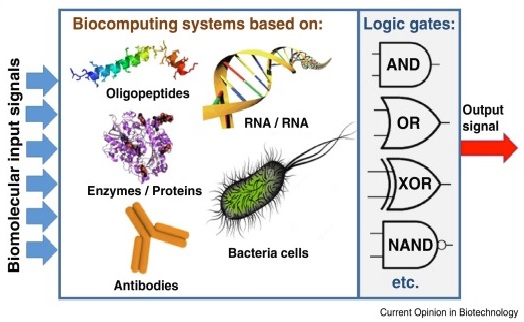
Security and Defense
The use of nano sensors for detection and identification of chemical and biological agents, explosives, and other hazardous materials.
Nanosensing is considered as most emerging field of application of nanotechnology. This may be due to its interesting utility in all possible areas of technological advancement. Nanosensors are comparatively newer and innovative devices which are being used multidisciplinary in many applications. Broadly applications of nanosensors can be listed in diverse areas such as pharmacy, biomedicine, agriculture, food, and security. In this chapter we will explore introduction to nanosensors, working, characteristics, applications, and future aspects. Different types of nanosensors, their working principle, fabrication and areas of applications, and recent developments have been incorporated in this chapter. Best attempt has been made to include nanosensors based on different technologies with emphasis on their applications.[1]

Figure .1 Security and Defense
Figure 1 shows Security and defense are areas that involve protecting countries, organizations, and individuals from internal and external threats, including physical, cyber, and biological threats.
Some of the current trends in security and defense include:
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning:The use of AI and machine learning technologies to improve threat detection and response, automate routine tasks, and enhance decision-making in areas such as surveillance, border control, and counterterrorism.
- Cybersecurity:The increasing importance of cybersecurity in protecting critical infrastructure, financial systems, and personal information from cyber-attacks and data breaches. This includes the use of advanced encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems, as well as the development of policies and regulations to promote cyber hygiene and resilience.
- Unmanned systems:The use of unmanned systems, such as drones and autonomous vehicles, in a range of security and defense applications, including reconnaissance, surveillance, and logistics. This technology can enhance situational awareness and reduce risks to human operators.
- Biometric identification:The use of biometric identification technologies, such as facial recognition and fingerprint scanning, to improve security and prevent identity fraud. These technologies can be used in areas such as border control, law enforcement, and access control to secure buildings and facilities.
- Space security:The growing importance of space security in protecting critical infrastructure and assets, such as satellites, from potential threats, including cyber-attacks and physical attacks from space-based weapons. This includes the development of policies and regulations to promote responsible behaviour in space, as well as the use of advanced technologies to monitor and detect potential threats.
These trends highlight the increasing complexity and interconnectedness of security and defense challenges, as well as the importance of innovation and collaboration in addressing these challenges. Ongoing research and development, as well as partnerships between government, industry, and academia, will be critical to developing effective security and defense solutions.
References:
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/B9780128207772000029
Cite this article:
Janani R (2023),Security and Defense, AnaTechMaz, pp.138