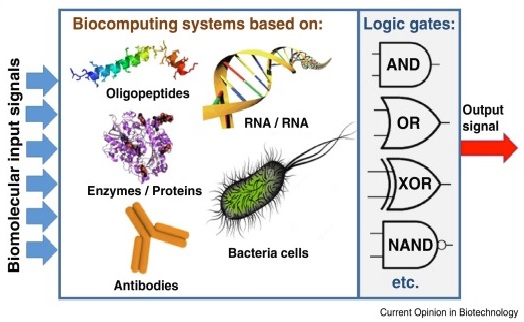
Biomineralization
Biomineralization is the process by which living organisms produce minerals within their tissues. The minerals produced can be organic, such as bone or tooth enamel, or inorganic, such as calcium carbonate shells or silica skeletons. Biominerals can be formed in various shapes, sizes, and structures, depending on the organism and its environment.
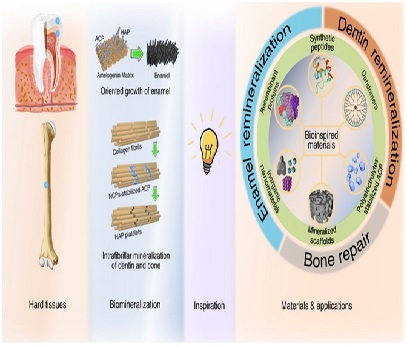
Figure 1. Biomineralization [1]
Biomineralization Process
Figure 1 shows biomineralization. The process of biomineralization typically involves a series of steps. First, the organism produces an organic matrix that serves as a template for mineral formation. The matrix can be a protein, such as collagen or keratin, or a carbohydrate, such as chitin or cellulose. The matrix can also contain other organic molecules, such as lipids or pigments, that help to control the mineralization process.
Next, the organism transports mineral ions, such as calcium, magnesium, or silica, from the environment into the site of mineralization. The ions can be transported actively or passively, depending on the organism and the environmental conditions. Once inside the site of mineralization, the ions are concentrated and organized in a way that promotes crystal formation and growth.
Finally, the crystal grows and becomes integrated into the organic matrix, forming a biomineral composite. The composite can be further modified by the organism to achieve the desired shape, structure, and properties. For example, some organisms can produce layered structures that enhance mechanical strength or optical properties.
Biomineralization is an important process in many biological systems. In marine organisms, biominerals can provide protection from predators and environmental stressors, as well as support for movement and feeding. In terrestrial organisms, biominerals can provide structural support, protection from physical damage, and storage of minerals. Biominerals can also play important roles in biochemical processes, such as ion transport, pH regulation, and enzyme catalysis.
Understanding the mechanisms of biomineralization is of great interest to scientists in many fields, including biology, chemistry, physics, materials science, and engineering. Biomineralization has inspired the development of novel materials and technologies, such as biomimetic materials, bioceramics, and bioinspired sensors. Biomineralization also has implications for the study of evolution, ecology, and biogeochemistry, as well as for the development of new biotechnologies and mineral resources.
References:
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41368-021-00147-z/figures/1
Cite this article:
Hana M (2023), Biomineralization, AnaTechMaz,pp.142