Future Structure of Genomics Technology
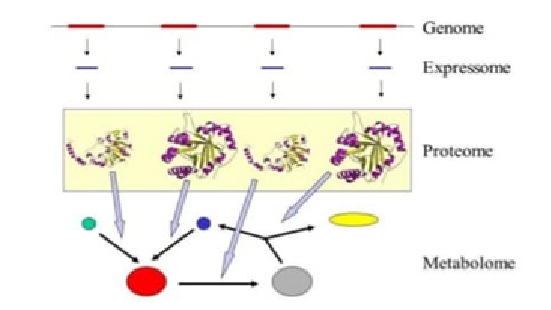
The mapping of the first human genome in 2000 heralded the start of the 21st century and introduced the century figure 1 shown below of genomics. Today, the ability to sequence genomes in research [1] labs is routine.

Figure 1: Future of Genomics Technology
DNA sequencing is rapidly entering clinical use for a wide array of applications, including reproductive health, cancer treatment, infectious disease diagnostics, and rare inherited disease. Large-scale national studies of human genomes around the world are rapidly increasing our understanding of how our genetic code drives human biology.
Wang leads engineering R & D at Illumina Inc., a company dedicated to improving human health by providing DNA sequencing tools for both research and clinical use.
Twenty years have passed since a new era in genomics began, initiated by the publication of the first draft of the human genome. Currently, DNA sequencing costs are [2] plummeting, gene therapy is making a comeback, ethical boundaries are being pushed to the limit by gene editing and new technologies like single cell and transcriptomics are creating a new wave of genomic breakthroughs.
How far the field of genomics has come over the last 20 years is not in question. But where the state of genomics will (or should) go from here is a hot topic of discussion.
The National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) has recently completed their 2020 strategic plan, the third of its kind. The vision for genomics, according to the authors, has never been clearer. The future, they say, lies in “responsible stewardship” and increasing diversity.
References:
- https://scienceandtechnology.jpl.nasa.gov/future-genomics
- https://www.genengnews.com/topics/omics/genomics/the-future-of-genomics/
Cite this article:
Nandhinidwaraka. S (2021) The Technology of Genomics, AnaTechmaz, pp 5