Types of Genomics Technology
Structural Genomics:
The structural genomics deals with DNA sequencing, sequence assembly, sequence organisation and [1] management. Basically, it is the starting stage of genome analysis i.e. construction of genetic, physical or sequence maps figure 1 shown below of high resolution of the organism.
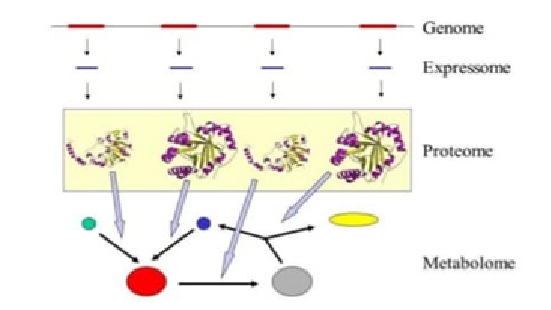
Figure 1: Types of Genomics Technology
Functional Genomics:
Based on the information of structural genomics the next step is to reconstruct genome sequences and to find out the function that the genes do. This information also lends support to design experiment to find out the functions that specific genome does. The strategy of functional genomics has widened the scope of biological investigations.
This strategy is based on systematic study of single gene/ protein to all genes/proteins. Therefore, the large-scale experimental methodologies (along with statistically analysed/computed results) characterise the functional genomics. Hence, the functional genomics provide the novel information about the genome.
Single Cell Genomics:
Based on single-cell genome analysis techniques, we can correctly identify cell types, which is critical in the fields of developmental biology and cell therapy. The histological description of cell types will be replaced by cell [2] typing based on the use of biomarkers and molecular profiles. Recent advances in single-cell RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptome analyses have vastly transformed our understanding of the cell types.
Types of Genetic Drift
The process of genetic drift can be categorized into two main types:
Bottleneck Effect
This type of genetic drift is characterized by the natural phenomenon of population elimination of the weaker allele.
In such cases, the population size severely decreases due to the factors of competition, predators, or diseases, indicating the concept of ‘survival of the fittest’.
Therefore, this elimination results in a change in the frequency of the allele.
Founder Effect
Under this effect, a new population emerges at some new location due to the specific habitat or the physical or geographical barriers.
Since this new population is not a part of the food cycle or the food web of that area, the allelic frequencies of the new population will be different from the original population.
References:
- https://www.biologydiscussion.com/genomics/genomics-meaning-types-and-classification-genetics/38127
- https://collegedunia.com/exams/genetic-drift-types-causes-and-examples-biology-articleid-1258
Cite this article:
Nandhinidwaraka. S (2021) The Technology of Genomics, AnaTechmaz, pp 3