Preventive Medicine and Fitness
Future space medicine will focus on preventive measures to maintain astronauts' health during extended missions. Regular exercise regimes and countermeasures will be essential to minimize muscle and bone loss. Advanced fitness equipment and techniques will help astronauts maintain their physical well-being and ensure their safe return to Earth.
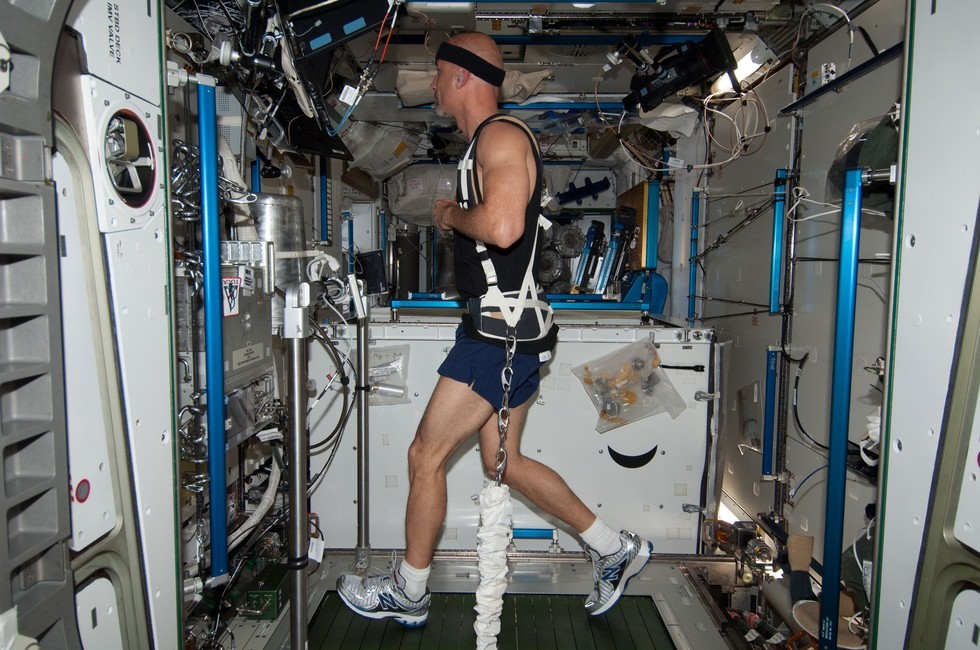

Figure 1.Preventive Medicine and Fitness
Figure 1 shows Long-duration spaceflight leads to a significant decrease in astronauts' exercise capacity, ranging from 30 to 50 percent. This decline occurs because both the heart and capillaries fail to deliver oxygen effectively to working muscles in microgravity. Researchers believe this reduction in cardiovascular function limits astronauts' ability to perform physically demanding activities. The study suggests that changes occur at both the heart level and within the capillaries, impacting the microcirculation.[1]
Preventive medicine and fitness are crucial aspects of space missions to maintain astronauts' health and well-being during their time in space.
Here are some key components:
Exercise Regimes: Astronauts follow strict exercise routines to counteract muscle and bone loss caused by the lack of gravity. Regular cardiovascular and resistance exercises, such as cycling, treadmill running, and resistance training, help preserve muscle strength and bone density.
Nutritional Planning: Proper nutrition is essential to support astronaut health and performance in space. Space agencies design balanced diets with the right mix of macronutrients and micronutrients to meet the unique physiological needs of astronauts in microgravity.
Monitoring Vital Signs: Continuous monitoring of astronauts' vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation, helps identify any health issues early and allows for timely interventions.
Psychological Support: Psychological well-being is critical for astronauts on long-duration missions. Counselling, support, and recreational activities are provided to help astronauts cope with isolation and confinement in space.
Sleep Management: Adequate and restful sleep is vital for astronaut performance and well-being. Sleep schedules are carefully managed to align with the 24-hour day and minimize sleep disturbances.
Infection Prevention: Strict hygiene protocols are followed to prevent the spread of infections in the confined space of the spacecraft or space station.
Countermeasure Research: Space agencies conduct ongoing research to develop new countermeasures to address health challenges in space, including the use of medications, supplements, and specialized equipment.
Post-Mission Rehabilitation: After returning to Earth, astronauts undergo rehabilitation programs to help them readjust to gravity and recover from any physiological changes experienced during their time in space.
By implementing preventive medicine and fitness programs, space agencies aim to optimize astronaut health and performance, ensuring their safety and success during space missions, especially for long-duration missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
References:
- https://www.space.com/36779-spaceflight-astronaut-fitness-blood-vessels-function.html
Cite this article:
Janani R (2023),The Future of Space Medicine: Healthcare for Astronauts, Anatechmaz,pp 2