Health Challenges in Space
The future of space medicine is crucial as humans venture into longer and more distant space missions. Space travel poses unique health challenges for astronauts due to microgravity, radiation exposure, isolation, and confinement. These factors can lead to various physiological changes, including bone density loss, muscle atrophy, fluid shift, and potential impacts on the cardiovascular and immune systems.

Figure 1.Health Challenges in Space
Figure 1 shows Health Challenges in Space Astronauts experience 10 times more radiation in space, damaging their immune systems and making them susceptible to infection. Long-term exposure can lead to cataracts and cancers due to cell and DNA damage. Dosimeters monitor radiation levels, and astronauts are restricted from working further in space once certain thresholds are reached. Space agencies like NASA are researching radiation effects and testing materials to protect astronauts from radiation in suits and spacecraft.[1]
Health challenges in space arise from the unique environment of microgravity and other factors that impact astronaut physiology.
Some key health challenges include:
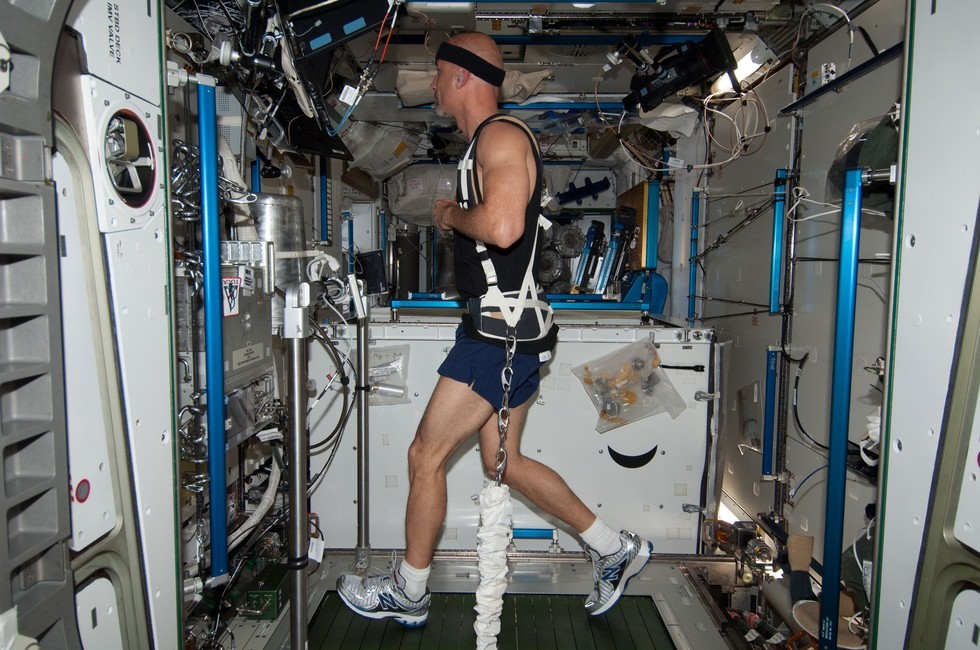
Musculoskeletal Issues: In the absence of gravity, astronauts experience muscle atrophy and bone density loss, leading to weaker muscles and bones. This can result in reduced physical performance and increased risk of fractures.
Cardiovascular Changes: The heart adapts to the microgravity environment, leading to changes in its shape and function. Prolonged exposure to microgravity can result in a decrease in cardiovascular fitness and orthostatic intolerance upon return to Earth.
Fluid Shifts: In microgravity, bodily fluids shift towards the upper body, leading to facial puffiness and reduced leg volume. This can affect the balance of fluids in the body and impact kidney function.
Vision Impairment: Some astronauts experience vision changes during their space missions, including an increase in intraocular pressure, optic disc swelling, and visual acuity issues. The exact cause of these vision impairments is not fully understood.
Radiation Exposure: Astronauts are exposed to higher levels of cosmic radiation and solar particles in space. This radiation can damage cells and DNA, increasing the risk of cancer and other long-term health effects.
Psychological Stress: Space missions involve isolation, confinement, and distance from loved ones, leading to psychological challenges such as depression, anxiety, and sleep disturbances.
Immune System Suppression: Prolonged exposure to space conditions can weaken the immune system, making astronauts more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
Addressing these health challenges is crucial to ensure the well-being and success of astronauts during space missions. Continuous research, medical monitoring, countermeasures, and advanced medical facilities are essential to mitigate these effects and pave the way for safe and sustainable human exploration beyond Earth.
References:
- https://www.lpi.usra.edu/education/explore/space_health/background/#:~:text=Astronauts%20receive%2010x%20the%20amount,leading%20to%20cataracts%20and%20cancers.
Cite this article:
Janani R (2023),The Future of Space Medicine: Healthcare for Astronauts, Anatechmaz,pp 1