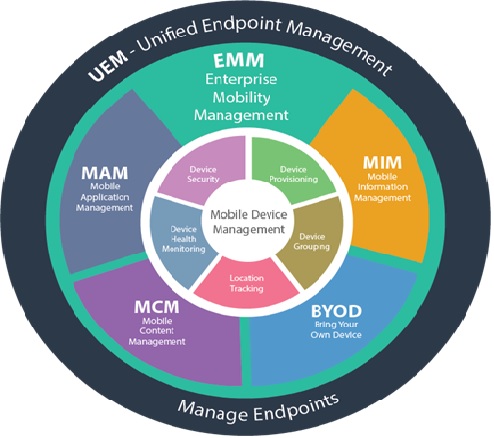
Technology Of Mobile Virtual Network Operator
A mobile virtual network operator or MVNO is a wireless communications service provider. Unlike traditional mobile network operators (MNOs), MVNOs do not own the infrastructure they use. Instead, they lease it from MNOs and use the infrastructure [1] to deliver a unique set of services to their markets. MVNOs acquire bulk access to an MNO’s services at discounted or wholesale rates and set retail prices for sale to consumers.
Tesco Mobile is an MVNO. It offers cell phones, call plans, and data as an MVNO. Tesco Mobile is able to be an MVNO by leveraging O2’s figure 1 shows below mobile network infrastructure.
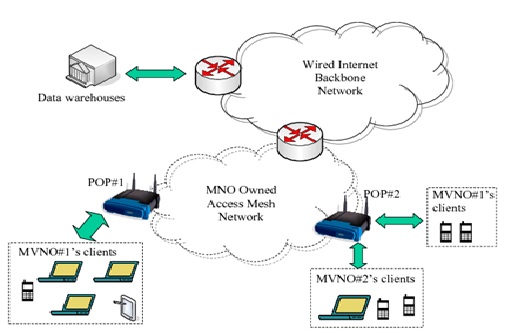
Figure1: Virtual Network Operator
- Access to a large existing base of consumers
- Loyal customers, making it easier to sell white-labeled mobile networks products and services
- Capital or access to capital to invest in front-end systems to cater to consumers (think marketing, sales, and customer services)
As a large multinational supermarket chain, Tesco has access to a large market of consumers. Using its name and reach, Tesco is able to leverage brand affinity to offer consumers an alternative to traditional mobile network deals.
And this is not the first time Tesco ventured into a new industry. They have done something similar in the financial sector, creating a bank in partnership with the Royal Bank of Scotland -- proof that brands wield a tremendous amount of power.
There are several reasons why mobile operators permit MVNOs on networks. For example, mobile operators generally find it hard to serve all customer segments; MVNOs can implement specific marketing to tackle targeted consumer groups. Most of the mobile operators have capacity, segment needs and products in new areas such as 3G. MVNOs help [2] ensure better network utilization. MVNOs also help mobile operators target customers with special service requirements. They provide low operational costs for mobile operators, grow average revenue per user and solve difficult issues regarding how to deal with fixed mobile convergence. MVNOs are also more able to try experimental applications and projects.
Types
- None
This is the usual setting, and means that this APN configuration is not restricted to use on a particular MVNO or subscriber account. [3]
When the type is set to None, the value field is not used.
- SPN
Indicates that the value to match is a SPN value (Service Provider Name).
- IMSI
Indicates that the value to match is an IMSI value (International Mobile Subscriber Identity). This value is unique to every subscriber account on any network world-wide.
- GID
Indicates that the value to match is a Group Identifier Level 1.
References:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mobile_virtual_network_operator#:~:text=A%20mobile%20virtual%20network%20operator%20%28%20MVNO%29%20is,over%20which%20it%20provides%20services%20to%20its%20customers.
- https://www.techopedia.com/definition/26081/mobile-virtual-network-operator-mvno
- https://tamingthedroid.com/mobile-virtual-network-operator-type
Cite this article:
S Nandhinidwaraka (2021) Technology of Mobile Virtual Network Operator, AnaTechmaz, pp. 27