Future of Long-Term Evolution (LTE)
The Long Term Evolution Market was valued at USD 10.78 billion in 2020 and is expected to reach USD 91.04 billion by 2026 and work at a CAGR of 42.69% over the forecast period 2021-2026. The continuous proliferation of smartphones across the world has increased the average data consumption by an average man, which has increased the need for LTE services, driving the market.[1]

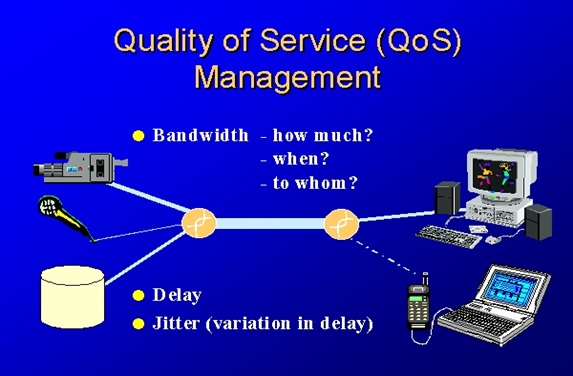
Figure 1. The future of long term evolution (lte)
Figure 1 shows an LTE network employs the multiuser variant of the orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) modulation scheme, called orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA), for its downlink signal.
OFDMA enables the LTE downlink to transmit data from a base station to multiple users at higher data rates than 3G, with improved spectral efficiency. Single-carrier FDMA is used for the uplink signal, which reduces the transmit power required of the mobile terminal.
The upper layers of LTE are based on Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol, which results in an all-Internet Protocol network, like that of wired communications. LTE supports mixed data, voice, video and messaging traffic.
LTE-A uses multiple input, multiple output (MIMO) antenna technology similar to that used in the IEEE 802.11n wireless local area network standard. MIMO and OFDM enable a higher signal-to-noise ratio at the receiver, providing improved wireless network coverage and throughput, especially in dense urban areas.
LTE-A requires devices to be fit with a special chip. Broadcom, Nvidia and Qualcomm all make chips that support LTE-A. Today, the vast majority of smartphones support LTE-A.[2]
Long Term Evolution (LTE) Market Overview:
Global Long term evolution (LTE) Market is forecast to reach $84.1 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 22.4% during the forecast period from 2021 to 2026. Rising adoption of smartphones have been driving the need for higher internet connectivity, wireless broadband connectivity, particularly 4G wireless broadband technology, thus causing higher adoption for LTE services.
Increasing adoption of long term evolution due to increasing data usage in demanding applications along with public safety LTE networks demands have been fueling the growth of LTE market.
Moreover, rising adoption of various industry verticals towards improving communication standards within the organization as well as high investments towards research and development from telecom sector has been causing significant market growth. The replacement of GSM, CDMA and UMTS with LTE technology will be a major market driver.[3]
Features:
LTE is designed for lower latency (the time it takes for data to travel in the network) and increased bandwidth - very interesting for the Internet of Things.
In fact, bandwidth increases can be as high as 100 Mbps on the downlink and up to 50 Mbps on the uplink.
- The higher bandwidth enables faster access to content and applications, particularly video applications that can only be offered today on fixed systems.
- The low latency enables time-sensitive applications like voice services.
- The all-IP architecture enables new converging services based on the IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS).[4]
References:
- https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/long-term-evolution-lte-market-growth
- https://searchmobilecomputing.techtarget.com/definition/Long-Term-Evolution-LTE
- https://www.industryarc.com/Report/44/global-long-term-evolution-lte-market.html
- https://www.thalesgroup.com/en/markets/digital-identity-and-security/technology/lte
Cite this article:
Thanusri swetha J (2021), Future of long term evolution (lte), AnaTechmaz, pp. 21