NASA Revises Impact Probability for Asteroid 2024 YR4: Will It Hit Earth?
Now that the full moon has passed, the darker skies allow astronomers to resume tracking asteroid 2024 YR4. Ground-based telescopes require minimal light pollution to detect these faint and elusive objects, as the brightness of a full moon can make observations nearly impossible.

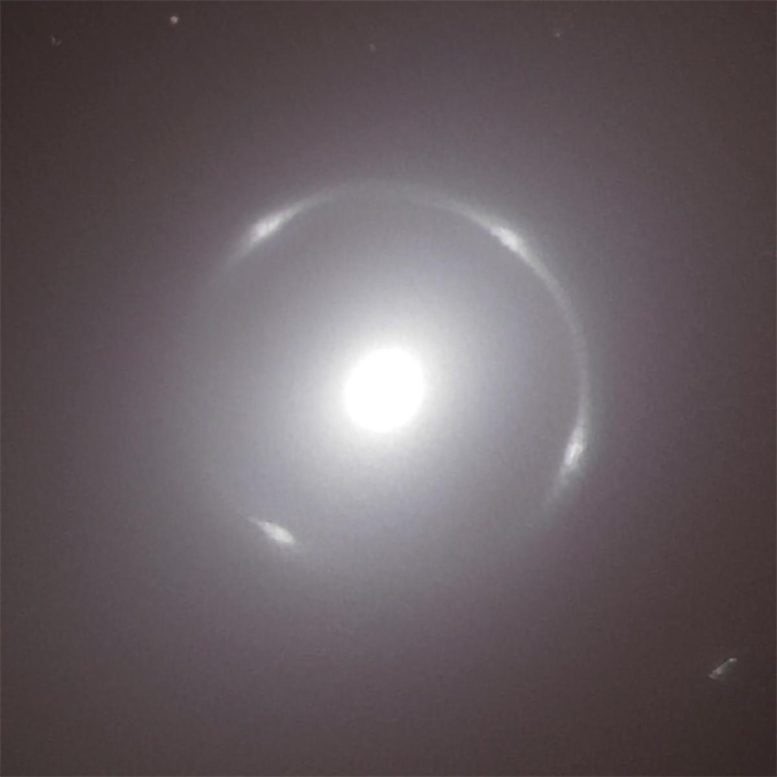
Figure 1. NASA Updates Impact Risk for Asteroid 2024 YR4: Potential Earth Approach.
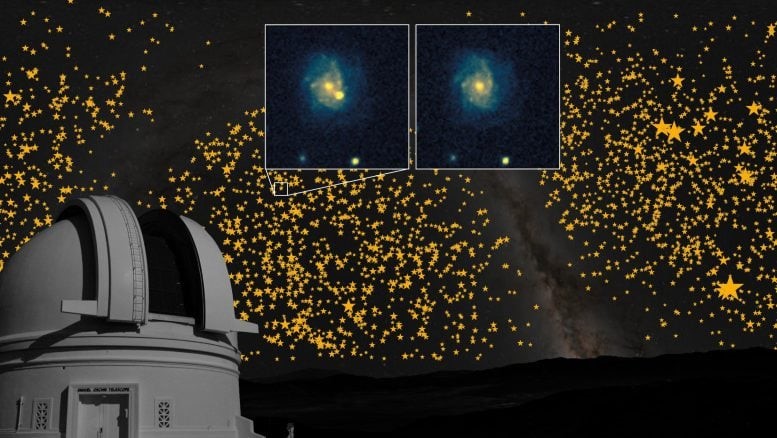
NASA’s Center for Near-Earth Object Studies (CNEOS) at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California has analyzed fresh data from the Minor Planet Center. On February 18, updated calculations estimated a 3.1% chance of asteroid 2024 YR4 impacting Earth on December 22, 2032—the highest probability ever recorded for an object of this size or larger. However, by February 19, new overnight observations refined the estimate, reducing the impact probability to 1.5%. Figure 1 shows NASA Updates Impact Risk for Asteroid 2024 YR4: Potential Earth Approach.
Refining the Asteroid’s Path
Each additional night of observations allows scientists to further refine the trajectory of asteroid 2024 YR4 and assess its potential risk to Earth. NASA anticipates that impact probability estimates will continue to evolve as more data becomes available in the coming days and weeks.
Recent observations have helped reduce uncertainty around the asteroid’s path. In the above graphics, the yellow dots indicate possible positions of the asteroid on December 22, 2032. As astronomers continue tracking its motion, this region of potential locations will shrink. For the impact probability to drop to zero, Earth must fall outside the asteroid’s possible range of positions on that date.
Potential Impact on the Moon
There is also a much lower chance that asteroid 2024 YR4 could impact the Moon, with current calculations estimating this probability at 0.8%.
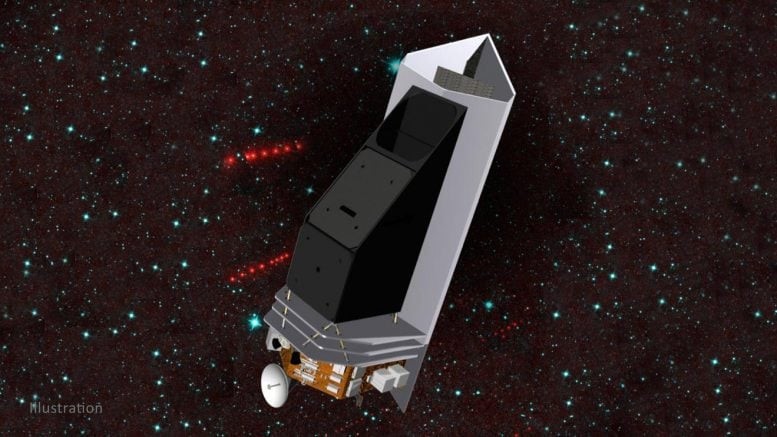
To improve asteroid detection, NASA’s Near-Earth Object Surveyor (NEO Surveyor) mission—scheduled for launch no earlier than September 2027—will enhance the search for previously unknown asteroids using infrared technology. Unlike visible light, which can make dark asteroids difficult to detect, infrared observations capture the heat emitted by these objects as they absorb sunlight. Additionally, NEO Surveyor’s space-based vantage point will complement ground-based observatories, improving our ability to track potentially hazardous asteroids.
Observing the Asteroid
With the full moon now past, astronomers have resumed observations of asteroid 2024 YR4. Ground-based telescopes require minimal light pollution to detect faint asteroids, and bright moonlight can hinder these efforts. Now that the skies are darker, scientists can gather more data to refine the asteroid’s trajectory.
Initial Impact Probability Estimates
NASA’s Center for Near-Earth Object Studies (CNEOS) analyzed data from the Minor Planet Center and, on February 18, estimated a 3.1% chance of impact on December 22, 2032. This was the highest recorded probability for an asteroid of this size. However, continued observations led to an updated calculation on February 19, lowering the impact probability to 1.5%.
Refining the Asteroid’s Path
Each night of observation helps scientists narrow down the asteroid’s possible trajectory. The yellow dots in NASA’s tracking graphics represent possible locations of 2024 YR4 on December 22, 2032. As more data is gathered, this uncertainty will decrease. For the impact probability to drop to zero, Earth must fall outside the asteroid’s range of possible positions on that date.
Potential Impact on the Moon
Aside from Earth, asteroid 2024 YR4 also has a small chance—estimated at 0.8%—of impacting the Moon. While significantly lower than the Earth impact probability, this scenario remains under observation.
Future Tracking and NASA’s NEO Surveyor Mission
NASA continues to track the asteroid and expects further refinements in its impact probability as new data becomes available. The upcoming Near-Earth Object Surveyor (NEO Surveyor) mission, set to launch no earlier than September 2027, will improve asteroid detection using infrared technology. This space-based observatory will complement ground-based telescopes, enhancing our ability to identify and monitor potentially hazardous objects.
Source: SciTECHDaily
Cite this article:
Priyadharshini S (2025), "NASA Revises Impact Probability for Asteroid 2024 YR4: Will It Hit Earth?", AnaTechMaz, pp. 237