4,000 Supernovae Could Transform Our Understanding of Dark Energy
Revealing the Unexpected Diversity of White Dwarf Supernovae
Astrophysicists have identified a surprising range of explosion patterns in white dwarf stars. By examining nearly 4,000 recorded events through a cutting-edge astronomical survey, researchers have gained new insights that may enhance cosmic distance measurements and expand our knowledge of dark energy.
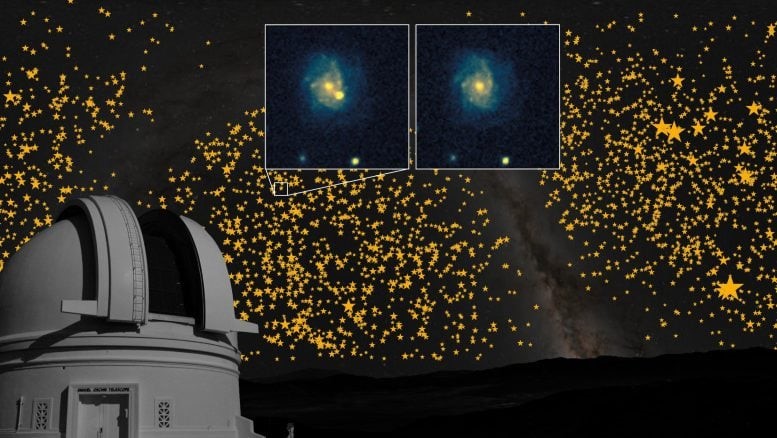

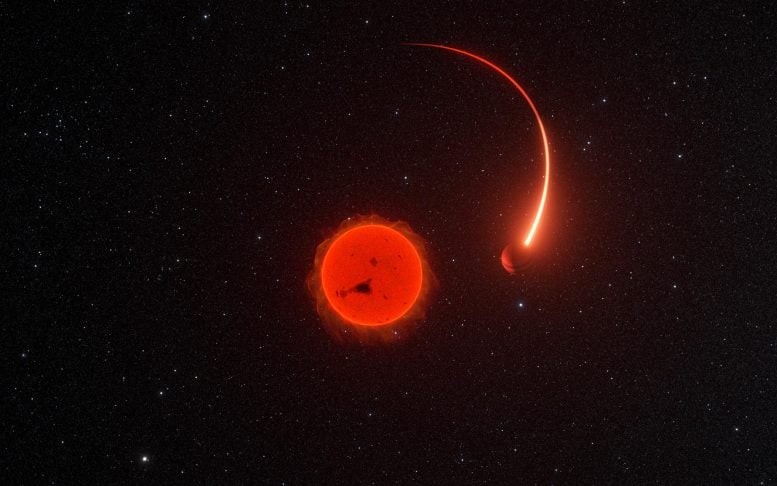
Figure 1. Unveiling Dark Energy: Insights from 4,000 Supernovae.
For decades, the catastrophic explosions of white dwarfs at the end of their lifecycles have been vital for studying dark energy—the enigmatic force behind the universe’s accelerating expansion. These supernovae also serve as cosmic forges, producing essential elements such as titanium, iron, and nickel under immense heat and pressure. Figure 1 shows Unveiling Dark Energy: Insights from 4,000 Supernovae.
Novel Pathways for White Dwarf Explosions
One of the key findings, led by the team at Trinity, is the discovery that white dwarfs can explode through multiple exotic mechanisms. These include dramatic collisions between two stars, producing luminous stellar displays, as well as instances where a white dwarf cannibalizes its companion in a double star system.
This breakthrough was made possible by the ability to detect extremely faint signals combined with the large dataset. The unexpected diversity of these explosions could have significant implications for using supernovae as cosmic distance markers, as the reliability of dark energy measurements depends on the ability to standardize these events.
A Wider Range of White Dwarf Explosions Than Expected
“The variety of ways white dwarf stars can explode is far greater than we previously thought, producing events that range from barely detectable faint flashes to brilliant explosions visible for months or even years,” says Prof. Maguire.
The Role of White Dwarf Supernovae in Cosmology
White dwarf supernovae, specifically Type Ia, have long been considered “standard candles” for measuring the expansion of the universe. Their consistent brightness allows scientists to estimate vast cosmic distances. However, this new study suggests that these explosions may not be as uniform as previously believed, raising questions about the accuracy of dark energy measurements.
Unexpected Diversity in Supernova Explosions
The study uncovered a surprising variety in how white dwarfs detonate. Some explode through collisions with other stars, while others undergo unique disruptions in binary systems. This variability could affect how we use these supernovae to track the universe’s accelerating expansion, requiring a reassessment of standardization methods.
The Challenge of Measuring Dark Energy
Dark energy is the mysterious force driving the acceleration of the universe’s expansion. Astronomers rely on precise supernova measurements to constrain its properties. If Type Ia supernovae are more diverse than assumed, scientists may need to refine their models to ensure accurate calculations of cosmic distances and expansion rates.
How Advanced Surveys Are Changing Our Perspective
The findings were made possible by next-generation astronomical surveys capable of detecting even the faintest supernovae. The combination of a vast dataset and improved observation techniques has provided an unprecedented look at the complexity of stellar explosions, revealing details that were previously overlooked.
The Future of Supernova Cosmology
With this new understanding, researchers are working to refine how they classify and standardize white dwarf supernovae. Future observations and theoretical models will be crucial for determining whether adjustments to dark energy measurements are needed. This study marks a turning point in cosmology, offering both challenges and new opportunities for understanding the fundamental forces shaping the universe.
Source: SciTECHDaily
Cite this article:
Priyadharshini S (2025), "4,000 Supernovae Could Transform Our Understanding of Dark Energy",AnaTechMaz, pp. 230