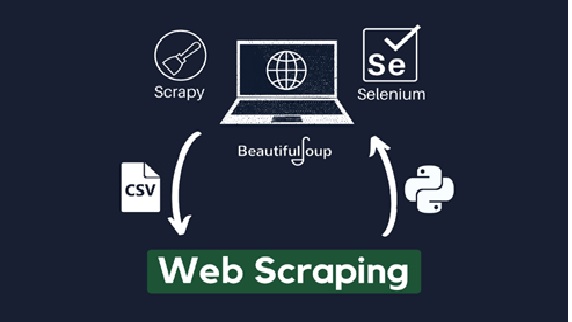
Technologies of Wi-Fi 7
Wi-Fi 7 is a new specification for Wi-Fi devices currently in the works. It’s based on the draft 802.11be standard, published in May 2021, that has not yet been finalized or approved by the FCC. The most show-stopping feature of Wi-Fi 7 is that it might make wired Ethernet connections obsolete for a certain class of both home users and professionals. Wi-Fi 7 can theoretically support bandwidth up to 30 gigabits per second (Gbps) per access point, which is just over three times as fast as the maximum 9.6 Gbps speed of Wi-Fi 6 (also known as 802.11ax). The draft authors call this “Extremely High Throughput,” or EHT.

Figure 1. The Technologies of Wi-Fi 7
Figure 1 shows it’s worth noting that Wi-Fi 7 is far from a formalized specification at this point. In fact, the Wi-Fi Alliance hasn’t even given it the Wi-Fi 7 moniker yet. Unsurprisingly then, you’re unlikely to find consumer devices offering support for it anytime soon. Work on the protocol is set to be completed in 2023 or 2024. And even then, you might have to wait another year or two for mainstream adoption.
Even though it has been a full year since Wi-Fi 6E was finalized, most countries have yet to delicense the new 6GHz spectrum for public use. According to this list compiled by the Wi-Fi Alliance, major markets like the US, UK, and EU countries have delicensed the spectrum, allowing it to be used for indoor applications. However, there are still some notable exceptions. Australia and Japan, for example, are still considering action, while other key markets like India haven’t responded to the industry’s demand at all.
Wi-Fi 7: faster, smarter, and with far less lag
Wi-Fi 6 was optimized for congestion and wireless efficiency, enabling your router to effectively communicate with dozens of wireless devices. Wi-Fi6E weaved in a dedicated 6GHz frequency, adding additional channels for high-bandwidth devices like mesh routers to communicate with one another. If you think of wireless communication as lanes on a freeway, WiFi 6E effectively added a dedicated HOV or commuter lane, allowing high-priority buses and ambulances their own traffic-free channel.
In the real world, though, cars moving down a freeway can re-route themselves to avoid congestion. Until now, Wi-Fi couldn’t. A Wi-Fi 6 router can communicate data on both the 2.4-GHz, 5-GHz, and 6-GHz channels simultaneously, but they’re all independent of one another.
References:
- https://www.howtogeek.com/782023/what-is-wi-fi-7/
- https://www.androidauthority.com/wi-fi-7-802-11be-3069524/
- https://www.pcworld.com/article/616905/the-smarter-faster-less-laggy-wi-fi-7-is-on-the-horizon.html
Cite this article:
Thanusri swetha J (2022), Technologies of Wi-Fi 7, AnaTechMaz, pp. 66