Structure Of Broadband Wireless Networks
Mobile WiBB, also called mobile broadband, provides high – speed broadband the connection from mobile phone service providers which is accessible from random locations. The locations are within the coverage area of the phone towers of mobile service provider and the connections are subject to monthly service plan [1] subscribed by the user. Mobile broadband can be costlier due to its portability. Also, they generally have varying or limited speed except in urban areas.
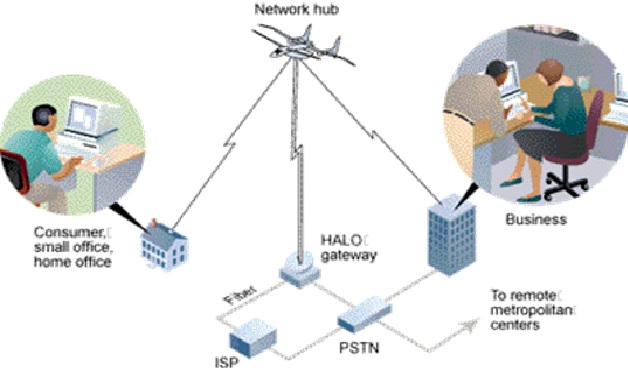
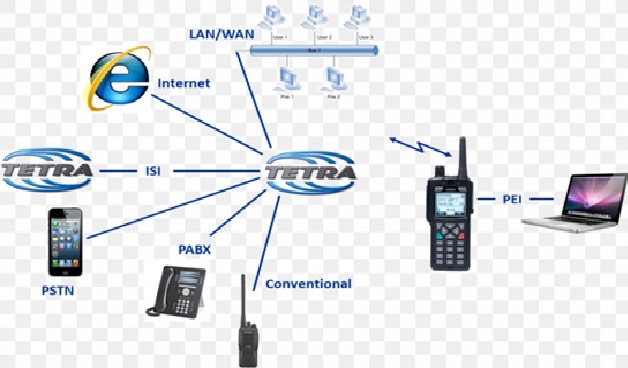
Wireless broadband (WiBB) a networking technology designed to impart highspeed Internet and data service through wireless networks. Wireless broadband figure 1 shown below may be delivered through wireless local area networks (WLANs) or wide area networks (WWANs).

Figure 1. Broadband Wireless Network
Wireless broadband is typically divided into either fixed or mobile categories, determined by if the connecting device is fixed in a single location or can be easily moved. A mobile connection would be in a cellphone, laptop or a dedicated mobile hotspot, and fixed wireless service would be a device designed to provide internet to an entire home or office.
Emerging Broadband, VoIP, and Wireless Services are all Packet-Based In the last decade there has been a lot of talk about broadband and VoIP, but it was mostly hype because the enabling technologies were not proven, and lacked bandwidth in the last mile infrastructure for broadband applications. Recently, the enabling technologies for broadband and VoIP are more mature. RBOC FTTx projects are building an infrastructure of higher bandwidth closer to home. MSOs are pushing triple play services. As service providers are rolling out [2] fiber access networks that can deliver higher bandwidth to the premises, IPTV with HDTV quality and VoIP applications become a reality. In the wireless arena, the IEEE broadband wireless access standard called 802.16 has existed for years, but only recently attracted a lot of attention because 802.16 uses an advanced radio technology (OFDM) scheme to span distances greater than 30 miles with a shared data rate up to 75 Mbps. This standard is more secure and provides better QoS when compared to other wireless technologies. The industry sees 802.16 as a disruptive technology for the wireless access network and provides a complement for wireline technologies such as DSL, cable, and FTTx. Most of the emerging broadband, VoIP, and wireless services are becoming packet-based. Analog TV signals are becoming digital MPEG packets. Traditional T1/T3/OC-n private lines are migrating to EPL, and VPN. Voice moves to VoIP. Broadband wireless data networks are emerging, with the goal of moving to an all-packetbased network. The vision of network convergence is coming back and is being driven by these emerging broadband wireline and wireless services plus the maturity of VoIP.
Broadband wireless works:
A mobile broadband network connects to [3] cellular towers through devices that are usually equipped with SIM cards. Let’s take a look at some examples:
SIM card slot
Devices that already have SIM card slots, such as your smartphone, can connect to mobile broadband networks without secondary devices, by plugging your service provider’s SIM into the device.
eSIM
Devices with eSIM (embedded SIM) can connect to a mobile broadband network without a secondary broadband device or a physical SIM card.
Dongles
These devices resemble thumb drives, and they plug into the USB drive of the device you want to connect. Dongles have SIM card slots where you plug in your telco’s SIM to make use of their service plan.
Pocket WiFi
These devices can also be described as dongles, but they don’t have to be plugged into your device’s USB port. Instead, they emit WiFi signals that you connect to, and can handle multiple connections unlike the traditional dongle which can only connect the device its plugged into.
Fixed Home Wireless Broadband
Some telcos provide fixed home wireless broadband devices that are just for the home (unlike pocket WiFi’s on-the-go approach). They emit WiFi signals to your devices.
References:
- https://www.tutorialspoint.com/what-is-wireless-broadband-wibb
- https://www.fujitsu.com/downloads/TEL/fnc/whitepapers/EmergingBroadband.pdf
- https://whatphone.com.au/guide/what-is-mobile-broadband-network
Cite this article:
S Nandhinidwaraka (2021) Structure Of Broadband Wireless Networks, AnaTechMaz, pp. 33