The Advantages and Challenges of Incorporating AI into Medical Decision-Making
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) found that an AI model achieved high accuracy on a medical quiz designed to evaluate the ability to diagnose patients based on clinical images and brief text summaries. However, physician-graders identified errors in the AI model's explanations of the images and its reasoning for arriving at the correct answers. These findings, which highlight both the potential and limitations of AI in clinical settings, were published in npj Digital Medicine. The study was conducted by researchers from NIH’s National Library of Medicine (NLM) and Weill Cornell Medicine, New York City.
“Integrating AI into healthcare offers significant promise as a tool to help medical professionals diagnose patients more quickly and initiate treatment sooner,” said Stephen Sherry, PhD, acting director of NLM. “However, as this study demonstrates, AI is not yet advanced enough to replace human experience, which remains crucial for accurate diagnosis.”
Figure 1. AI in Medical Decision-Making
The AI model and human physicians answered questions from the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM)’s Image Challenge, an online quiz featuring real clinical images and brief text descriptions detailing patient symptoms and presentation. Participants are asked to select the correct diagnosis from multiple-choice options. Figure 1 shows AI in Medical Decision-Making.
Researchers assigned the AI model 207 Image Challenge questions, requiring it to provide a written rationale for each answer. The prompt instructed that the rationale should include a description of the image, a summary of relevant medical knowledge, and a step-by-step explanation of how the model arrived at its answer.
Nine physicians from various institutions, each specializing in different medical fields, were recruited to answer the questions. They first completed the quiz in a “closed-book” setting (without external resources) and then in an “open-book” setting (using external resources). Afterward, the researchers provided the physicians with the correct answers, the AI model’s answers, and its rationale. The physicians were then asked to evaluate the AI model's performance in describing the images, summarizing relevant medical knowledge, and explaining its reasoning.
The study found that both the AI model and the physicians performed well in selecting the correct diagnosis. Notably, the AI model achieved a higher rate of correct diagnoses than physicians in the closed-book setting. However, physicians using open-book resources outperformed the AI model, particularly on the more challenging questions.
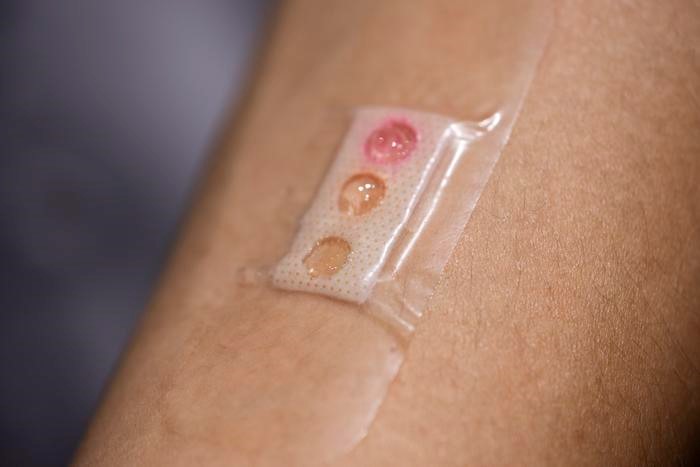
Importantly, physician evaluations revealed that the AI model frequently erred in describing medical images and explaining its reasoning, even when it correctly identified the diagnosis. For instance, in one case, the AI model was shown a photo of a patient’s arm with two lesions. Although a physician would recognize that both lesions were caused by the same condition, the AI model struggled because the lesions appeared differently due to their angles, creating an illusion of varying colors and shapes. As a result, the AI model failed to connect the lesions to the same diagnosis.
The researchers emphasize the need for further evaluation of multi-modal AI technology before its clinical implementation.
“This technology has the potential to enhance clinicians’ capabilities with data-driven insights, potentially leading to improved clinical decision-making,” said Zhiyong Lu, PhD, NLM Senior Investigator and corresponding author of the study. “Understanding the risks and limitations of this technology is crucial for effectively harnessing its potential in medicine.”
The study utilized GPT-4V (Generative Pre-trained Transformer 4 with Vision), a multimodal AI model capable of processing both text and images. The researchers acknowledge that, while this is a small study, it highlights the potential of multimodal AI to assist physicians in medical decision-making. Further research is necessary to better understand how such models measure up against physicians' diagnostic capabilities.
References:
- https://www.labmanager.com/the-risks-and-benefits-of-integrating-ai-into-medical-decision-making-32567
- https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2024/07/240723123334.htm
Cite this article:
Janani R (2024), The Advantages and Challenges of Incorporating AI into Medical Decision-Making, AnaTechMaz, pp.277