Types of Electric Relays
Relays are electrically operated switches that open and close the circuits by receiving electrical signals from outside sources. Some people may associate “relay” with a racing competition where members of the team take turns passing batons to complete the race. The “relays” embedded in electrical products work in a similar way; they receive an electrical signal and send the signal to other equipment by turning the switch on and off.
For example, when you push the button on a TV remote to watch TV, it sends an electrical signal to the “relay” inside the TV, turning the main power ON. There are various types of relays used in many applications to control different amounts of currents and number of circuits.[1]
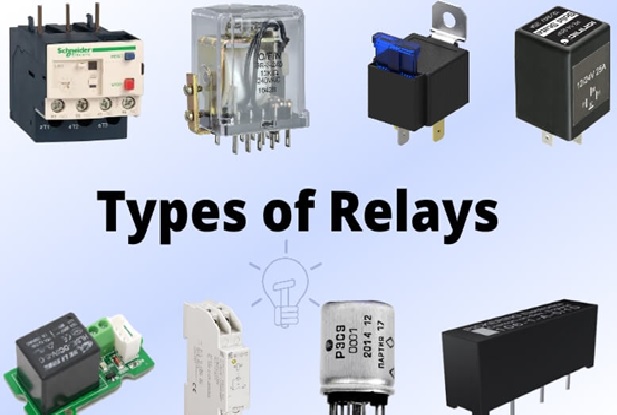
Figure 1. The Types of Electric Relays
Figure 1 shows the Relays are normally used in the control panels, manufacturing and building automation to control the power along with switching the smaller current values in a control circuit. However, the supply of amplifying effect can help control the large amperes and voltages because if low voltage is applied to the relay coil, a large voltage can be switched by the contacts. [2]
Types of Relays
There are different types of relays like:
- Electromagnetic Relays
- Latching Relays
- Electronic Relays
- Non-Latching Relays
- Reed Relays
- High-Voltage Relays
- Small Signal Relays
- Time Delay Relays
- Multi-Dimensional Relays
- Thermal Relays
- Differential Relays
- Distance Relays
- Automotive Relays
- Frequency Relays
- Polarized Relays
- Rotary Relays
- Sequence Relays
- Moving Coil Relays
- Buchholz Relays
- Safety Relays
- Supervision relays
- Ground Fault Relays [3]
A relay is an electrically operated switch. Many relays use an electromagnet to operate a switching mechanism mechanically, but other operating principles are also used. Relays are used where it is necessary to control a circuit by a low-power signal (with complete electrical isolation between control and controlled circuits), or where several circuits must be controlled by one signal. The first relays were used in long distance telegraph circuits, repeating the signal coming in from one circuit and re-transmitting it to another. Relays were used extensively in telephone exchanges and early computers to perform logical operations.
A type of relay that can handle the high power required to directly control an electric motor or other loads is called a contactor. Solid-state relays control power circuits with no moving parts, instead using a semiconductor device to perform switching. Relays with calibrated operating characteristics and sometimes multiple operating coils are used to protect electrical circuits from overload or faults; in modern electric power systems these functions are performed by digital instruments still called "protective relays". [4]
References:
- https://components.omron.com/relay-basics/basic
- https://www.electgo.com/what-is-a-relay/
- https://www.electronicshub.org/classification-of-relays/
- https://www.seminarstopics.com/seminar/692/electric-relays
Cite this article:
Thanusri swetha J (2021),Types of Electric Relays, Anatechmaz, pp. 72