The Small Golden Device That Just Broke Data Speed Records
Scientists have created an advanced plasmonic modulator that facilitates optical data transmission at groundbreaking terahertz frequencies. This breakthrough promises to revolutionize 6G networks, computing, and medical imaging by significantly enhancing data transfer speeds and efficiency.
- The modulator transforms electrical signals into optical signals for ultra-fast data transmission.
- Researchers at ETH Zurich set a new record, surpassing one terahertz in frequency.
- This innovation improves fiber-optic network efficiency by processing data at unprecedented speeds.
- Potential applications include next-generation mobile communications (6G) and other high-speed data transfer technologies.
Breaking the Terahertz Limit
Plasmonic modulators are miniature devices that transform electrical signals into optical signals for transmission through optical fibers. Until now, no such modulator had exceeded the terahertz threshold—equivalent to over a trillion oscillations per second. However, researchers at ETH Zurich, led by Professor Jürg Leuthold, have now achieved this milestone. Previously, similar modulators were limited to frequencies of 100 to 200 gigahertz, making this advancement five to ten times faster.
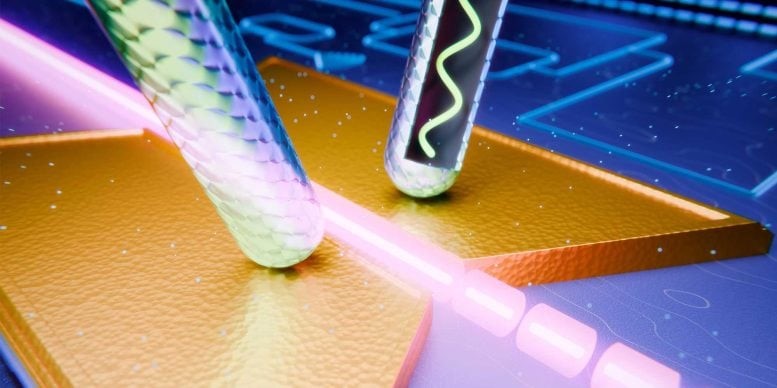
Figure 1.Small Golden Device.
These modulators are essential for linking electronic and optical communication, enabling the rapid transfer of massive data volumes. “Data is initially in electrical form, and at some stage, its transmission relies on optical fibers,” explains Professor Leuthold. Figure 1 shows small golden device.
Powering the Next Generation of 6G Networks
The upcoming 6G networks will operate in the terahertz spectrum, with optical fiber technology forming the backbone that connects base stations. “Our modulator enables the direct and efficient conversion of radio and other electrical signals into optical signals,” says Yannik Horst, who played a key role in this breakthrough during his doctoral research.
Beyond Telecommunications: A Multi-Purpose Innovation
Although transferring terahertz signals via optical fibers is already feasible, existing methods are intricate, costly, and require multiple components. This new modulator simplifies the process, lowering energy consumption and enhancing measurement precision [1]. Unlike traditional systems that need separate components for different frequency ranges, this advanced modulator functions across a vast spectrum—from 10 megahertz to 1.14 terahertz. “With a single, highly adaptable component, we cover the entire frequency range,” Horst emphasizes, showcasing its potential far beyond telecommunications.
Expanding Applications and Commercial Viability
In addition to telecommunications, this groundbreaking modulator has significant potential in optical fiber data transmission for high-performance computing centers. It also holds value for cutting-edge measurement technologies, including medical imaging, spectroscopic material analysis, airport security scanners, and radar systems—many of which already operate in the terahertz range.
Cutting-Edge Design and Market Readiness
This state-of-the-art modulator is a nanoscale structure composed of multiple materials, including gold, leveraging the interaction between light and free electrons within the metal [2] . Developed at ETH Zurich, the device was manufactured by Polariton Technologies, an ETH spin-off originating from Professor Leuthold’s research group. The company is currently working to bring the terahertz modulator to market, setting the stage for its widespread adoption in future data transmission and measurement technologies.
Reference
- https://scitechdaily.com/the-tiny-gold-device-that-just-shattered-data-speed-records/
- https://techxplore.com/news/2025-03-tiny-component-bandwidth-modulator-terahertz.html
Cite this article:
Keerthana S (2025),The Small Golden Device That Just Broke Data Speed Record, AnaTechMaz,pp.115