Revolutionizing Ammonia Production: A Sustainable Breakthrough for Agriculture and Beyond
In a groundbreaking development, researchers at UNSW Sydney have unveiled a revolutionary technique that promises to transform the production of ammonia for fertilizers. Traditionally notorious for its staggering carbon footprint, ammonia production is undergoing a sustainable makeover thanks to this innovative low-cost, low-energy, and environmentally friendly technology.

Figure 1. Agriculture.
The Carbon Footprint Challenge
Figure is for illustration purpose only. Historically, ammonia production has been synonymous with high-energy processes, contributing significantly to global carbon emissions. The conventional methods involve temperatures exceeding 400°C and pressures surpassing 200 atmospheres, accounting for 2% of the world's energy consumption and 1.8% of its CO2 emissions. This unsustainable approach has long been a concern for environmentalists and sustainability advocates.
The Sustainable Solution
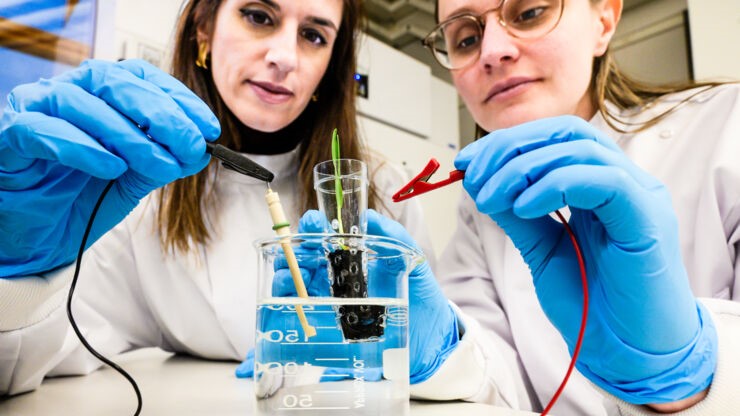
The researchers at UNSW Sydney have successfully developed a method that not only enhances energy efficiency but also renders environmentally friendly ammonia economically feasible. Unlike the traditional high-temperature, high-pressure processes, this new technique eliminates these requirements and reduces the need for extensive infrastructure in ammonia production.
Published Findings and Commercialization
The results of this groundbreaking research have been published in the journal Applied Catalysis B: Environmental. Moreover, the foundation of this research has already been licensed to PlasmaLeap Technologies, an Australian industry partner, through the UNSW Knowledge Exchange program. With a prototype ready for deployment, the technology is poised to enter the Australian agriculture industry, offering a sustainable alternative for ammonia production.
Advancements and Commercial Profitability
Building on proof-of-concept research conducted three years ago, the latest study showcases significant advances in energy efficiency and production rates. These improvements not only enhance the commercial profitability of the process but also position it as a viable and scalable solution for sustainable ammonia production.
Green Ammonia's Role in Hydrogen Transport
The research opens up new possibilities for utilizing green ammonia in the hydrogen transport market. Liquid ammonia (NH3) has the advantage of storing more hydrogen in a smaller space compared to liquefied hydrogen (H2), making it a more economical option for the transportation of hydrogen energy.
Tackling Climate Goals
The traditional ammonia production process, known as the Haber-Bosch process, is notorious for its energy intensity and reliance on fossil fuels. Dr. Ali Jalili, the leader of the study, emphasizes the importance of adopting a sustainable approach to ammonia production to align with global net zero objectives. The traditional method accounts for 2.4 tonnes of CO2 per tonne of ammonia, contributing to approximately 2% of global carbon emissions.
Addressing Supply Chain Disruptions
In addition to its environmental benefits, the sustainable production of ammonia addresses critical challenges related to international supply chain disruptions and geopolitical issues. The shortage of ammonia-based fertilizers impacts food security and production costs, making the need for a sustainable solution even more urgent.
Australia's Renewable Energy Initiatives
Dr. Jalili envisions a pivotal role for ammonia in Australia's renewable energy initiatives, positioning the country as a leader in renewable energy exports and utilization. The potential for hydrogen energy storage and transportation further strengthens ammonia's significance in the pursuit of sustainable energy solutions.
As the world strives to meet ambitious climate goals, the UNSW Sydney research marks a significant step forward in sustainable technology. The shift towards decentralized and energy-efficient ammonia production not only addresses environmental concerns but also offers a promising solution for agriculture, energy storage, and transportation, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient future.
Source: University of New South Wales
Cite this article:
Hana M (2023), Revolutionizing Ammonia Production: A Sustainable Breakthrough for Agriculture and Beyond, AnaTechmaz, pp. 242