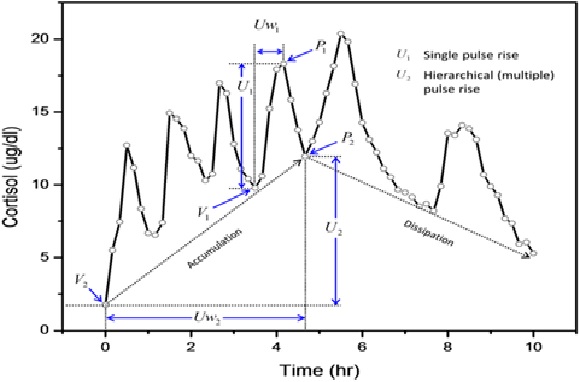
Biopharmaceuticals
Biopharmaceuticals are drugs that are produced using biological processes, such as genetic engineering, recombinant DNA technology, and cell culture. These drugs are made from living cells and are used to treat a variety of diseases, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, and rare genetic diseases.
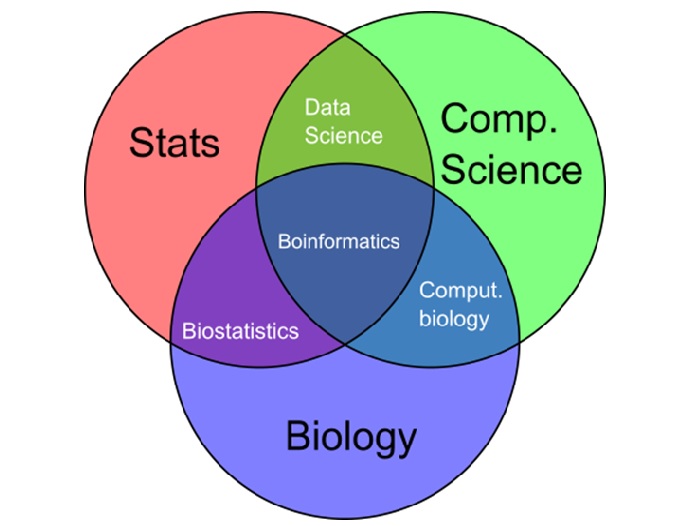
Figure 1. Biopharmaceuticals [2]
Figure 1 shows biopharmaceuticals. The first such substance approved for therapeutic use was recombinant human insulin (rHI, trade name Humulin), which was developed by Genentech and marketed by Eli Lily in 1982. [1]
The large majority of biopharmaceutical products are pharmaceuticals that are derived from life forms. Small molecule drugs are not typically regarded as biopharmaceutical in nature by the industry. However members of the press and the business and financial community often extend the definition to include pharmaceuticals not created through biotechnology. That is, the term has become an oft-used buzzword for a variety of different companies producing new, apparently high-tech pharmaceutical products. [1]
The biopharmaceutical industry and its bioprocessing sector are healthy and continue to grow in size/revenue, breadth, importance and diversity. Worldwide sales of biopharmaceuticals are now more than $300 billion, increasing at an annual rate of about 12% annually. This growth has been relatively consistent during the past 15+ years, which is why the segment is attractive to investors, explains Eric Langer, President and Managing Partner, BioPlan Associates [2]
Some topics related to biopharmaceuticals include:
- Monoclonal antibodies: These are antibodies that are designed to target specific proteins in the body and are used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and other conditions.
- Recombinant proteins: These are proteins that are produced using genetic engineering techniques and are used to treat a variety of diseases, including diabetes and hemophilia.
- Gene therapy: This is a type of treatment that involves inserting genes into a patient's cells to treat or prevent a disease.
- Biosimilars: These are drugs that are similar to existing biopharmaceuticals but are produced by different manufacturers.
- Cell therapy: This is a type of treatment that involves using living cells to treat diseases, such as cancer.
- Personalized medicine: This is an approach to medicine that involves tailoring treatments to a patient's genetic makeup.
- Drug delivery systems: These are systems that are designed to deliver biopharmaceuticals to specific parts of the body, such as tumors.
- Manufacturing processes: The production of biopharmaceuticals requires specialized manufacturing processes, including cell culture, fermentation, and purification.
- Regulatory issues: Biopharmaceuticals are subject to strict regulations by government agencies, such as the FDA, to ensure their safety and effectiveness.
- Intellectual property: Biopharmaceuticals are often protected by patents, which can create legal issues for manufacturers and competitors
References:
- https://www.bioprocessonline.com/doc/what-is-biopharmaceutical-0001
- https://www.manufacturingchemist.com/news/article_page/Trends_and_opportunities_in_biopharmaceutical_product_development_and_manufacturing/170557
Cite this article:
Hana M (2023), Biopharmaceuticals, AnaTechMaz, pp.122