Common Injuries and Wound Care
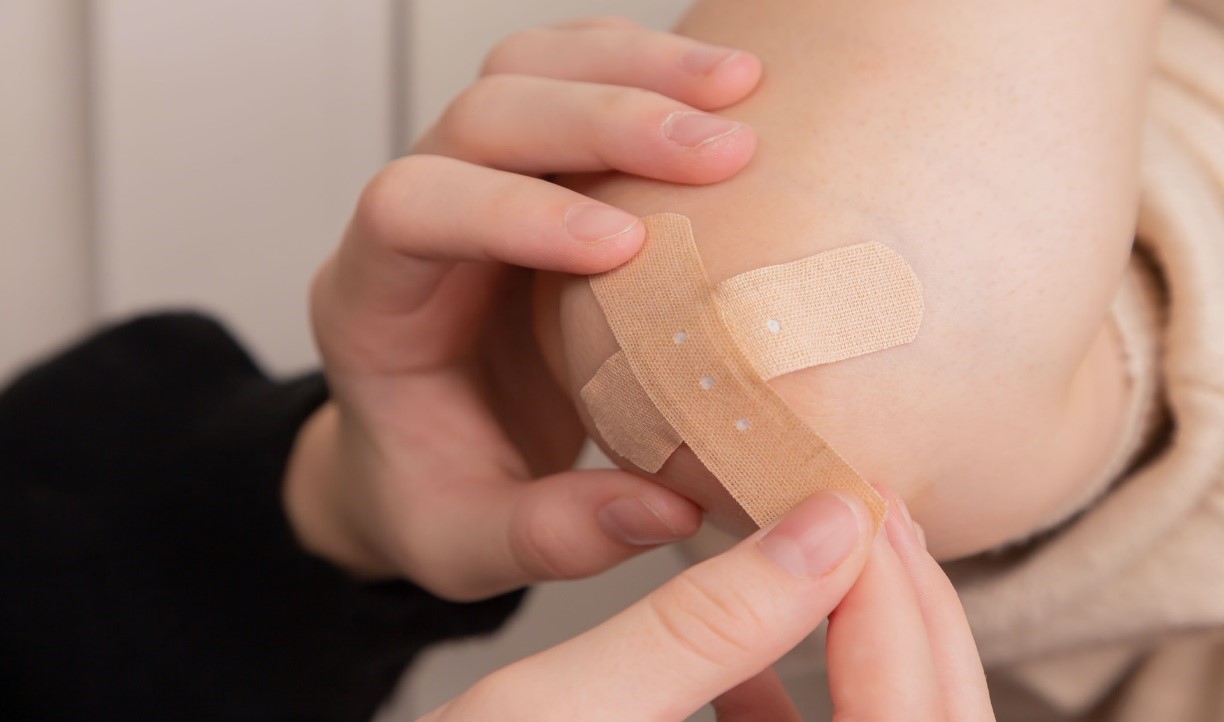
Figure 1. Wound Care.
Figure 1 shows wound care. Welcome to the second part of our First Aid 101 series. In this segment, we'll explore how to manage common injuries and provide proper wound care.
Step 4: Wound Care
Wounds can vary in severity, from minor cuts and scrapes to deeper injuries. Here's how to provide effective wound care:
Cleanse the Wound: Use clean water and mild soap to gently clean the wound. If available, you can also use antiseptic wipes to help prevent infection.
Control Bleeding: For minor cuts, apply gentle pressure using a clean cloth or bandage to control bleeding. If bleeding is severe, continue applying pressure and seek professional medical help.
Apply an Antiseptic: If you have antiseptic ointment or cream, apply it to the wound to reduce the risk of infection.
Cover the Wound: Use a sterile adhesive bandage or dressing to cover the wound. This protects the wound from dirt and further contamination.
Change Dressings: Regularly change the dressing and keep an eye on the wound for signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or pus. [1]
Step 5: Fractures and Sprains
Injuries involving bones and joints require special care:
Fractures (Broken Bones): If you suspect a fracture, keep the injured area as still as possible. Immobilize the fracture by splinting the injured area with materials like boards, rolled-up newspapers, or clothing.
Sprains and Strains: For sprains (ligament injuries) and strains (muscle/tendon injuries), use the R.I.C.E. method:
- R - Rest: Rest the injured area to prevent further damage.
- I - Ice: Apply a cold compress to reduce swelling and pain.
- C - Compression: Use an elastic bandage to provide gentle compression to the area.
- E - Elevation: Elevate the injured limb to reduce swelling.
Step 6: Burns and Heat-Related Injuries
Burns can result from various sources, including heat, chemicals, or electricity:
Heat Burns: For minor burns, cool the burned area with cold water for about 10 minutes to alleviate pain and prevent the burn from worsening. Cover the burn with a sterile non-stick dressing. [1]
Chemical Burns: Remove any contaminated clothing and flush the affected area with running water for at least 20 minutes. Seek medical attention for chemical burns.
Heat-Related Injuries: In cases of heat exhaustion or heat stroke, move the person to a cooler place, loosen tight clothing, and offer water to drink. Use cold compresses to help cool them down.
Remember, while these steps can be helpful in managing common injuries, seeking professional medical help is important, especially for more severe injuries. In the next part of our series, we'll delve into how to respond to specific medical emergencies, such as choking, seizures, and allergic reactions.
References:
- https://nhcps.com/lesson/cpr-first-aid-traumatic-injuries/
Cite this article:
Hana M (2023), First Aid 101, AnaTechmaz, pp.2





