NASA Captures the Intense X1.1 Flare in Action During Solar Storm Watch
NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory registered a notable solar flare on May 9, 2024, reaching its peak at 1:44 p.m. ET. The observatory, dedicated to Sun surveillance, successfully documented this event. This occurrence comes after X-class solar flares were also observed on May 7 and May 8. This particular flare is categorized as an X1.1 flare, with the "X" denoting the most severe flares, while the number offers further insight into its intensity.
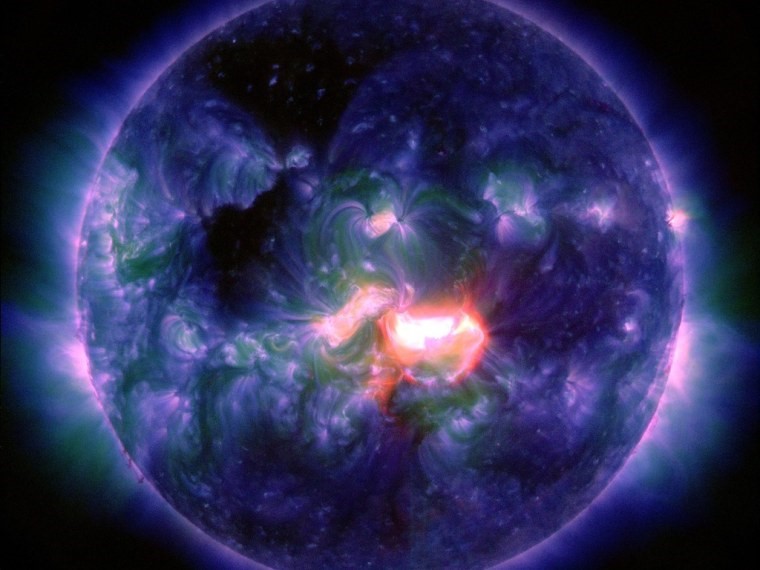

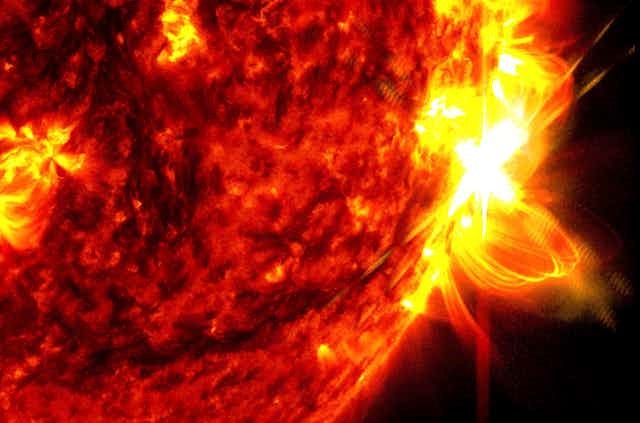
Figure 1. Solar Flare Captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory on May 9, 2024
Solar Eruptions
Figure 1 Shows Solar Flare Captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory on May 9, 2024.Solar flares represent intense bursts of radiation originating from the release of magnetic energy associated with sunspots. These eruptions constitute one of the most potent forms of solar activity and primarily consist of photons spanning radio waves to gamma rays. Occurring within the Sun's atmosphere, they manifest as bright areas on the solar surface, with durations ranging from minutes to hours.
Solar flares are classified based on their brightness in x-ray wavelengths, denoted by the classes A, B, C, M, and X, where A represents the weakest and X denotes the strongest. Each class exhibits a tenfold increase in energy output compared to the preceding one. Moreover, within each class, there exists a finer scale ranging from 1 to 9, providing a more precise quantification of the flare's strength. For instance, an X1 flare is ten times as potent as an M1 flare but notably weaker than an X9 flare. This classification system aids scientists and relevant authorities in assessing potential impacts on Earth, such as disruptions in communication and navigation systems, and formulating appropriate responses.
The Solar Dynamics Observatory of NASA
NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO), launched in February 2010 as part of the Living With a Star (LWS) program, serves a primary mission of comprehending the Sun's impact on Earth and near-Earth space. It achieves this by scrutinizing the solar atmosphere across small scales of space and time and in numerous wavelengths simultaneously. SDO plays a pivotal role in furnishing detailed insights into the Sun's activity, encompassing phenomena such as solar flares, coronal mass ejections (CMEs), and magnetic fields.
Outfitted with a suite of instruments, SDO captures high-resolution imagery of the Sun in 13 distinct wavelengths at intervals of mere seconds. This encompasses ultraviolet, extreme ultraviolet, and visible light spectra, facilitating meticulous observations of the solar atmosphere. The data amassed by SDO proves indispensable for comprehending solar variations impacting life on Earth and space-based technological systems. Moreover, the observatory aids scientists in unraveling the intricate dynamics of the Sun, thus enhancing the accuracy of solar weather prediction endeavors.
Source: SciTechDaily
Cite this article:
Janani R (2024), NASA Captures the Intense X1.1 Flare in Action During Solar Storm Watch, AnaTechMaz, pp.19