Quantum Computing Is Being Used to Clean Up the Environment
Carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere continue to rise on a daily basis, with no signs of abating or slowing. Too much of civilization is based on the use of fossil fuels, and even if a substitute energy source can be developed, much of the harm has already been done. Without removal, the existing carbon dioxide in the atmosphere will continue to cause havoc for generations.[1]
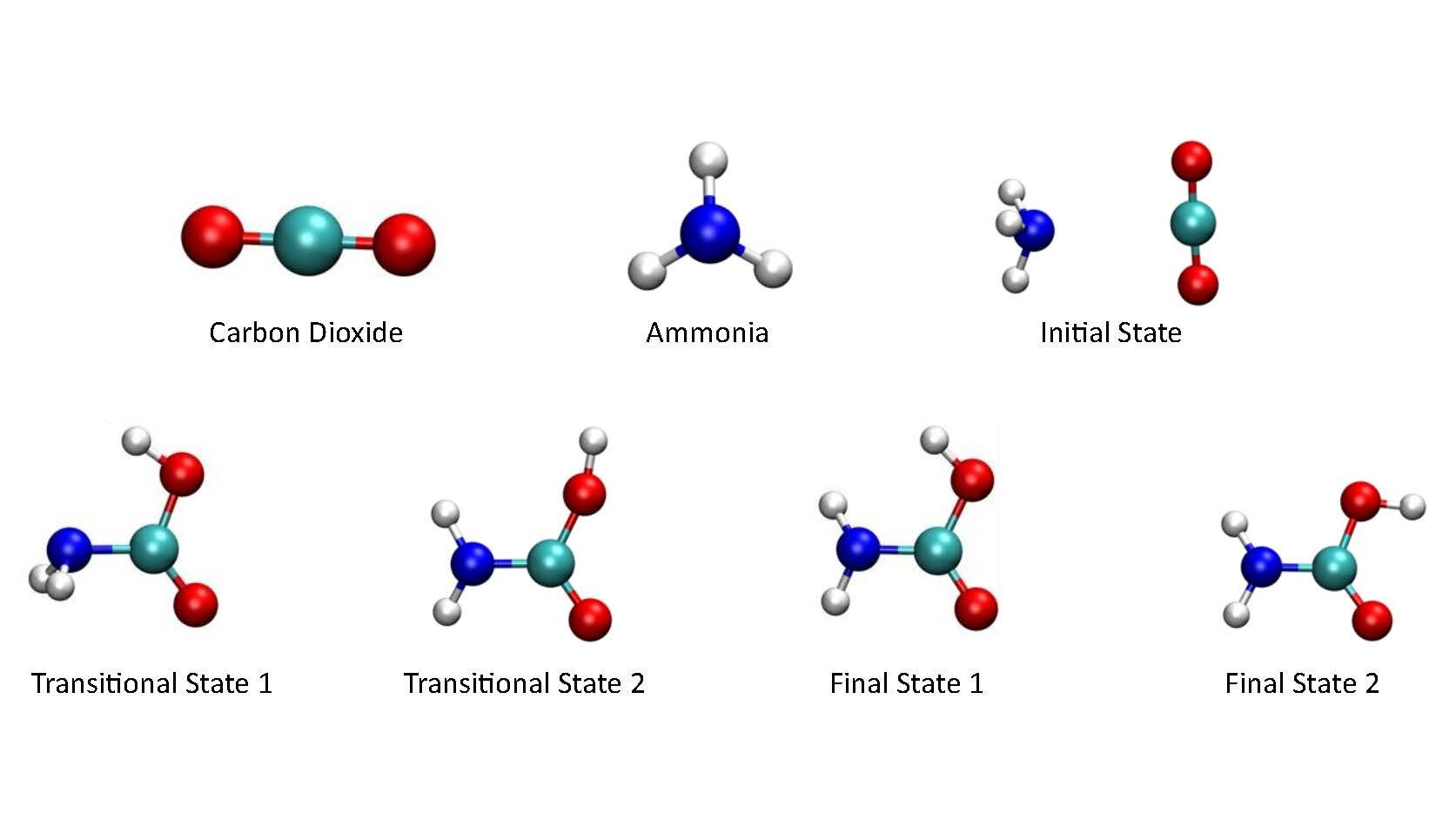
Figure 1. Quantum Computing Is Being Used to Clean Up the Environment
Figure 1 shows Atmospheric carbon capture has the potential to address the problem of increasing carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere. This technology aims to remove carbon dioxide from the air and store it permanently, thereby mitigating the effects of climate change. Currently, practical carbon capture technologies are still in the early stages of development. Among the most promising approaches is the use of amines, a class of compounds that can chemically bind with carbon dioxide. The focus is on improving the efficiency of these designs, as even slight advancements in identifying better compounds could result in capturing billions of additional tons of carbon dioxide.
Researchers from the National Energy Technology Laboratory and the University of Kentucky published an article in AVS Quantum Science on March 14. In their study, they utilized an algorithm deployed on a quantum computer to investigate amine reactions for carbon capture. The algorithm enables the identification of useful amine compounds for carbon capture in a more efficient and accelerated manner. By leveraging quantum computing, the researchers aim to expedite the discovery of effective amine compounds for carbon capture applications.
Author Qing Shao expressed dissatisfaction with the current amine molecules used in carbon capture processes. Shao highlighted the costliness of testing new molecules using classical computing resources. Therefore, the researchers aim to develop a fast algorithm that can efficiently screen thousands of new molecules and structures for carbon capture applications. The goal is to find improved amine compounds for carbon capture while reducing the computational burden and time required for testing.
Computer algorithms simulating chemical reactions must consider the interactions between every pair of atoms involved. Even a relatively simple reaction between a three-atom molecule like carbon dioxide and the four-atom ammonia can result in hundreds of atomic interactions. Traditional computers struggle with handling such complex calculations, but quantum computers are well-suited to tackle these challenges. Their ability to handle intricate atomic interactions makes them particularly effective in solving these types of problems related to chemical reactions.
While quantum computers are still in the process of development and not yet powerful enough to directly handle simulations of complex chemical reactions, the group's algorithm provides a solution. The algorithm enables existing quantum computers to analyse larger molecules and more intricate reactions, which is crucial for practical applications in fields such as carbon capture. By leveraging the algorithm, quantum computers become capable of tackling the challenges associated with simulating complex reactions, thereby advancing their utility in various domains.
Author Yuhua Duan expressed the objective of using the current quantum computing technology to address a practical environmental issue. The research aims to apply quantum computing to solve real-world problems, particularly in the realm of environmental concerns. By leveraging quantum computing technology, the researchers are striving to make valuable contributions towards finding solutions for pressing environmental challenges.
References:
- https://phys.org/news/2023-03-atmosphere-quantum.html
Cite this article:
Janani R (2023), Quantum Computing Is Being Used to Clean Up the Environment, AnaTechMaz, pp.119