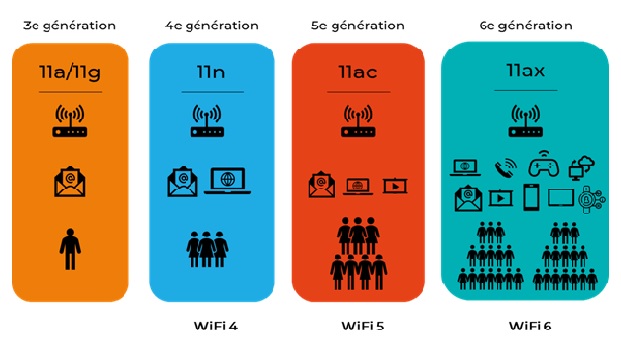
Platform Of Metro Optical Network
Metro Ethernet is an Ethernet transport network that provides point-to-point or multipoint connectivity services over a metropolitan area network (MAN). Ethernet originated as a LAN technology, and became a replacement for low-speed WAN technologies.
An Optical Network is basically a communication network used for the exchange of information through [1] an optical fiber figure 1 shown below cable between one end to another. It is one of the quickest networks used for data communication.
Figure 1: optical network
Business, residential, and mobile subscribers select Ethernet services from service providers because of its cost effectiveness, flexibility, and simplicity. Service providers use Metro Ethernet to:
- Interconnect business offices or data centers. Metro Ethernet can connect two sites or hundreds of sites.
- Connect residential subscribers or businesses to the Internet.
- Provide connectivity to public or private cloud data centers.
- Provide wholesale mobile backhaul services.
- Provide multicast delivery used by business customers for video conferencing, and used by residential subscribers for IPTV and video applications.
Reconfigurable WDM Network with ROADMs
- Static WDM engineering rules and scalability can be quite complex (OADM in every node) [2].
- Bandwidth and wavelength pre-allocation
- Margin allocation for fixed filter structure
- Insufficient power management
- Network extension requires Optical-Electrical-Optical (OEO) regeneration
- SDH/SONET networks are easy to plan.
- Access to entire bandwidth at every ADM
- Easy engineering rules (single hop only)
- Easy addition of new network elements
- A reconfigurable optical layer enables the following.
- On-demand bandwidth planning
- Extended transparent reach due to power management per WDM channel
- Hitless scalability
From a communications perspective, the landscape is fundamentally changing. Market dynamics associated with the changing enterprise services mix, 5G, cloud—as well as residential and data center connectivity—are creating new use cases and exciting revenue growth opportunities for service providers [3]. Consumer traffic flows are shifting heavily toward the home to support Small Office Home Office (SOHO), gaming and e-learning. Enterprises are accelerating their digital transformation and moving toward Virtualized Network Functions (VNFs) and cloud applications, including Software-Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN), to reduce costs. Deployment decisions for 5G are beginning to pick up as providers evaluate xHaul upgrade options and plan their evolution from 4G to 5G.
References:
- https://www.juniper.net/us/en/research-topics/what-is-metro-ethernet.html
- https://www.tutorialspoint.com/optical_networks/optical_networks_roadm.htm
- https://www.ciena.com/insights/what-is/what-is-ip-and-metro-convergence.html
Cite this article:
S Nandhinidwaraka (2021) Platform of Metro Optical Network, AnaTechMaz, pp. 30