New Aquabots Soft Robots Made of Liquids
Researchers at Hong Kong University (HKU) and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory have recently created Aquabots, a new class of soft robots that are predominantly made of liquids. As most biological systems are predominantly made up of water or other aqueous solutions.
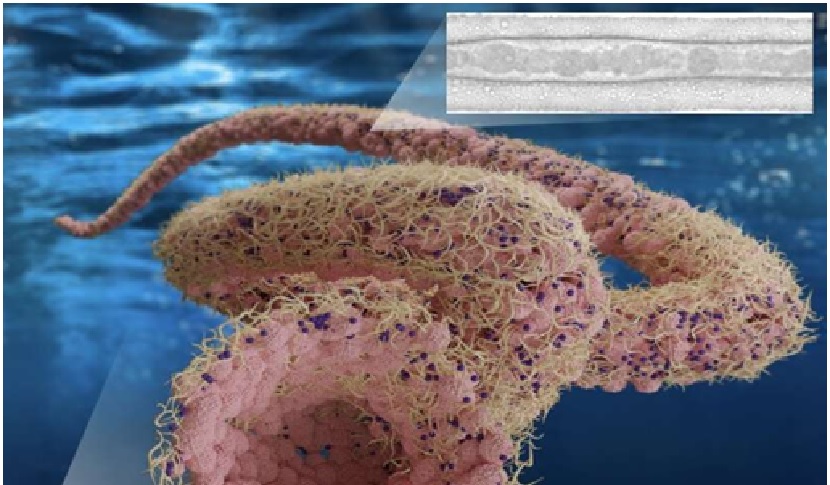
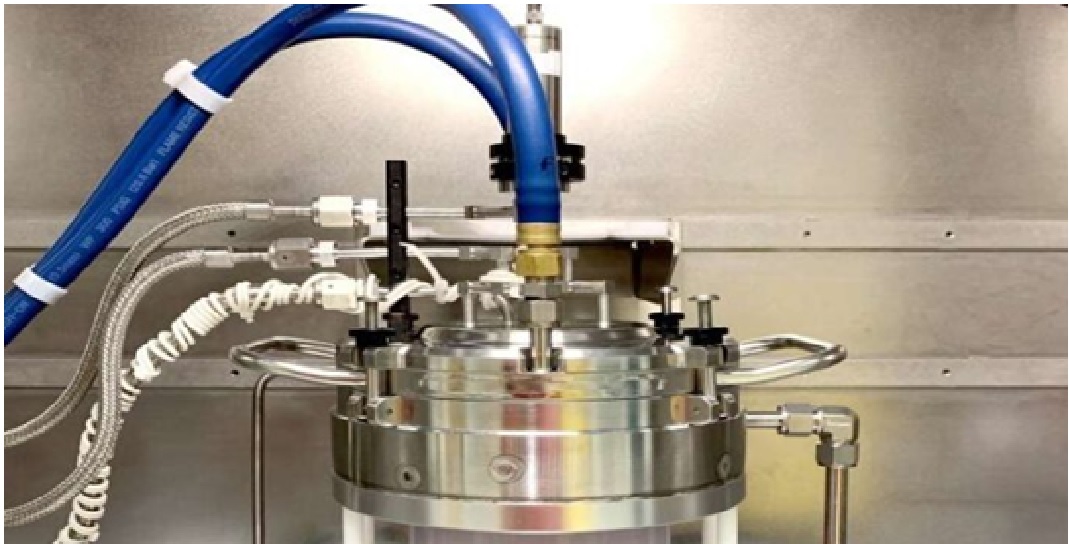
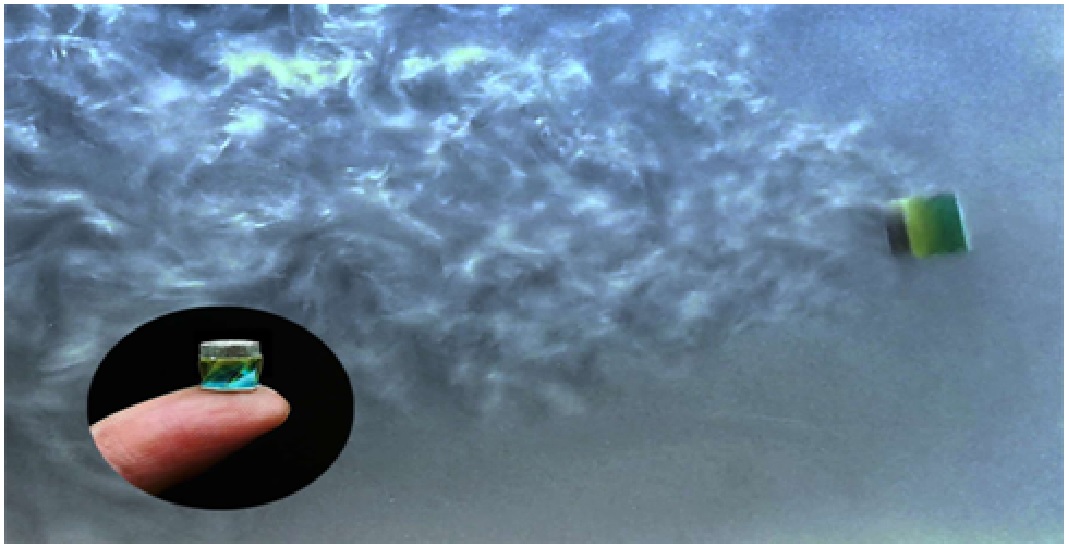
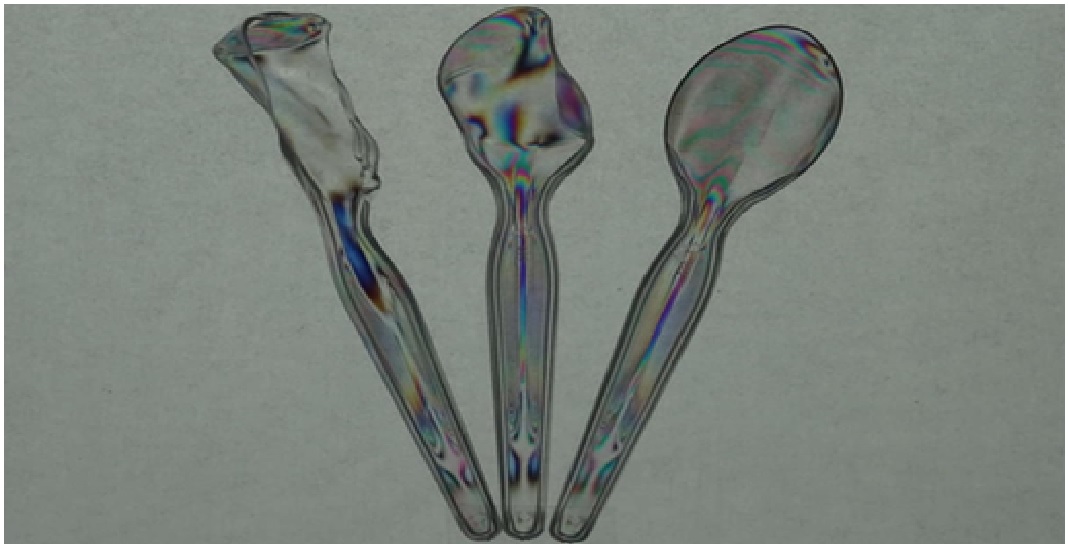
Figure 1. Aquabots - a new class of soft robots, made up of liquids.
Figure 1 shows thatShum, Russell, Zhu and their colleagues coupled all-liquid 3D printing techniques with aqueous two-phase assemblies (ATPS), strategies for assembling 3D structures, to realize artificial constructs that mimic biological systems. ATPS are a key area of focus for the research group at HKU led by Professor Shum. [1]
Researchers said, “our idea was to assemble the materials that the interface and the assemblies lock in the shapes of the liquids. The shapes are dictated using external forces to generate arbitrary shapes or to use all-liquid 3D printing to be able to spatially organize the assemblies.”
At the time, started pondering on the possibility of integrating magnetic nanoparticles into ATPS assembly systems. This would allow them to direct the motion of the ATPS constructs using external magnetic fields, which would produce robotic systems that are ultra-soft, flexible and can be adapted for specific functions.
The robots introduced by this team of researchers were assembled in aqueous environments. This means that they can operate in aqueous environments and can also be adapted to complete specific tasks using water-soluble compounds. [2]
The Aquabot designs presented in the team’s recent paper are very simple, as they are a prototype that demonstrates how they can be assembled. However, in the future, this same process could be used to create more complex structures that can solve more complex problems.
In the future, Aquabots could open up exciting possibilities for many real-world biomedical and environmental applications. For example, they can be used to deliver drugs to specific locations inside Human body for biological engineering of human tissues and for artificial performance of functions of certain biological systems.
Shum said, “our next works should also explore other properties and functions provided by the Aquabot platform, beyond the proof-of-concept of the mechanical manipulation and chemical reactions demonstrated in the paper. It would be interesting to combine this with other microfluidic and robotic approaches for new applications.” [3]
References:
- https://techxplore.com/news/2022-08-aquabots-ultrasoft-liquid-robots-biomedical.html
- https://coderbabu.in/aquabots-ultrasoft-liquid-robots-for-biomedical-and-environmental-applications/
- https://illinoisusanews.com/ultrasoft-fluidic-robots-for-biomedical-and-environmental-applications/51489/
Cite this article:
Sri Vasagi K (2022), New Aquabots Soft Robots Made of Liquids, AnaTechMaz, pp.284