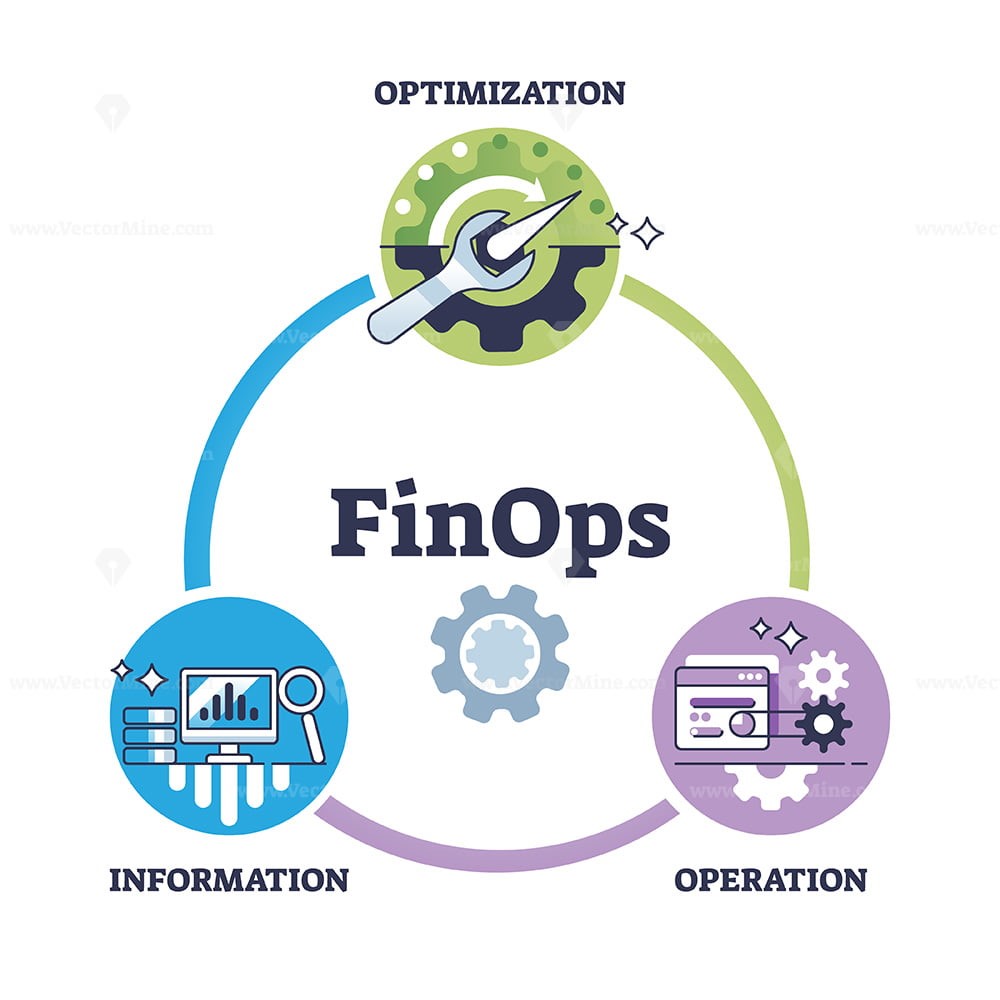
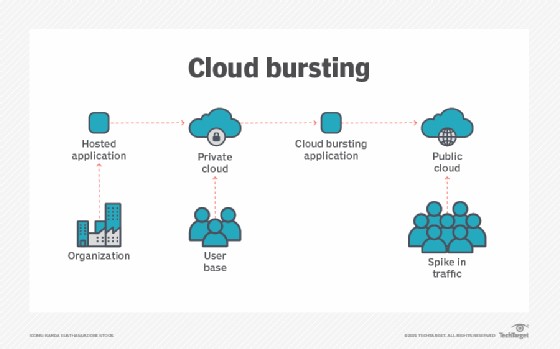
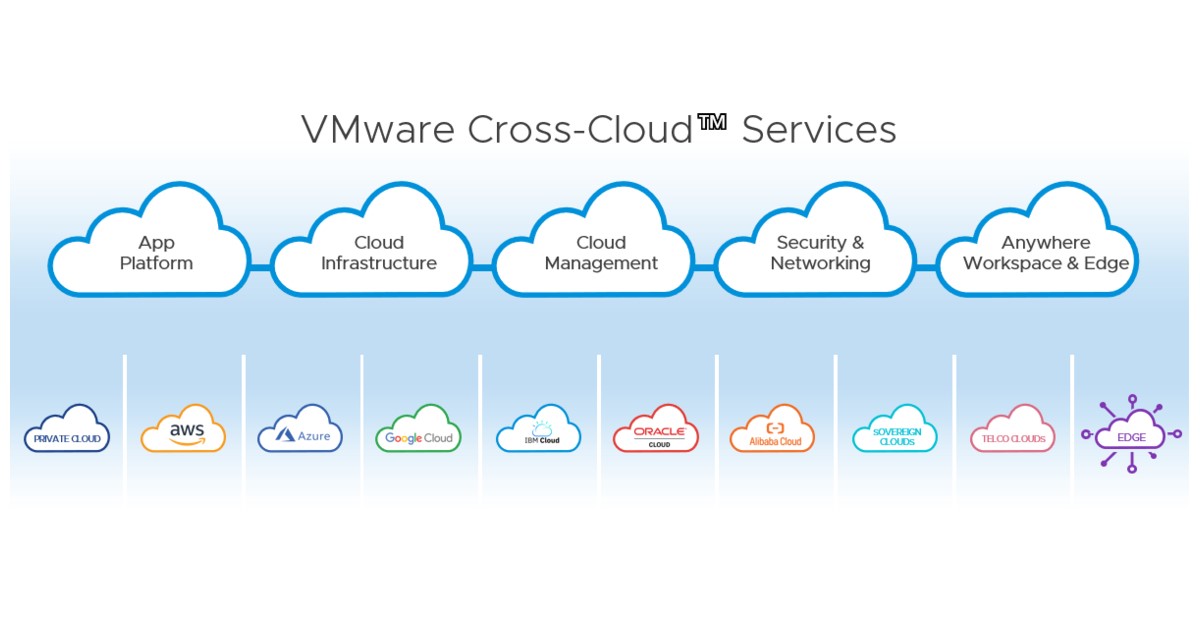
XaaS cloud offerings mature
“Anything as a service” (XaaS) describes a general category of services related to cloud computing and remote access. It recognizes the vast number of products, tools, and technologies that are now delivered to users as a service over the internet. Essentially, any IT function can be transformed into a service for enterprise consumption. The service is paid for in a flexible consumption model rather than as an upfront purchase or license.
Figure 1. XaaS cloud offerings mature
XaaS cloud offerings mature is shown in Figure 1. Because XaaS stands for “anything as a service,” the list of examples is endless. Many kinds of IT resources or services are now delivered this way. Broadly speaking, there are three categories of cloud computing models: software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and infrastructure as a service (IaaS).
Drawbacks of XaaS
As is with every other technology, there are always downsides. So let’s have a look at XaaS’s drawbacks.
Vulnerable to Internet Anomalies: XaaS runs on the internet, and the latter’s glitches make XaaS prone to downtime. Various anomalies would stunt XaaS’s full potential, from internet outages to bandwidth fluctuations. It is wise to invest in a reliable VPN connection to avoid these issues.
Unforeseen Complexities: Not everyone is current with the latest technologies, and should a problem arise, it is tough to troubleshoot if none knows the underlying technology of XaaS. It is pertinent to educate the staff about the methodology and technology. [2]
Common Types of Offerings under XaaS
XaaS brings together various infrastructures. However, the frequently used ones are listed below
- SaaS – Like Google Apps, Microsoft Office 365, Salesforce: such software applications can be provided through SaaS to its users.
- PaaS – Like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Elastic Beanstalk, Heroku, Force.com, Google App Engine, Apache Stratos: all of them provide resources (preconfigured virtual machines (VMs) as well as other resources) for application development.
- IaaS – Like Microsoft Azure, Google compute engine, AWS elastic compute cloud: organisations can deploy and configure VMs hosted in the vendor’s data center as well as manage those VMs remotely via IaaS.
- StaaS (Storage as a Service, also denoted as SaaS) – Provision of application, backup as well as data storage systems in the cloud.
- DBaaS (Database as a Service) – Provision access to database-platform through the cloud. Public providers AWS, as well as Azure, have DBaaS offerings.
- MaaS (Malware as a Service) – Like VMWare AppDefence: make use of the public cloud to help organisations for robust protection from common cyber attacks (Ransomeware, Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS), etc.).
- Emerging technologies like these are other examples of XaaS – Network as a Service (NaaS), Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS), Communications as a Service (CaaS). Additionally, some of today’s brick and mortar businesses can also be included in XaaS, where real life services (like transportation, food delivery, etc.) are provided via leveraging digital technologies (Examples: Uber, Swiggy, etc.).[3]
References:
- https://www.netapp.com/cloud-services/what-is-anything-as-a-service-xaas/
- https://www.veritis.com/blog/understanding-xaas-everything-as-a-service-and-its-advantages/
- https://vipointsolutions.net/series-on-latest-open-source-technology-trends-5/
Cite this article:
Gokula Nandhini K (2023), XaaS cloud offerings mature, AnaTechMaz, pp.94