The Aerial-Aquatic Hybrid Drone
A groundbreaking collaboration between Professor Ben M. Chen from The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) and Professor Jie Chen from Tongji University's Shanghai Research Institute for Intelligent Autonomous Systems has resulted in the creation of the TJ-FlyingFish. This unprecedented amphibious drone, launched in early February 2023, marks a game-changing advancement in exploration capabilities, opening up new frontiers in underwater environments. Its remarkable features make it a versatile tool with immense potential across a wide range of industries. [1]
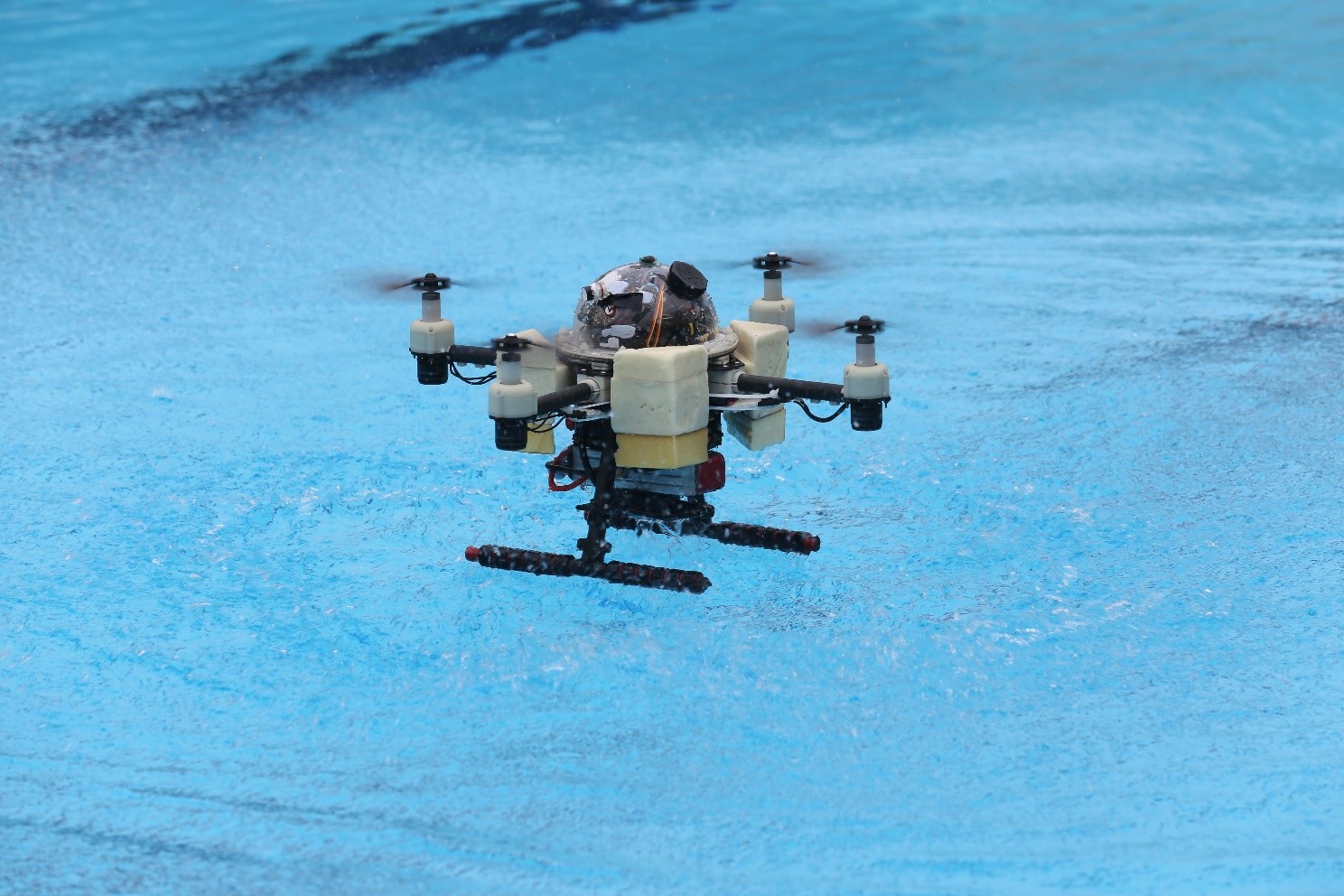
Figure 1. The Aerial-Aquatic Hybrid Drone
Can be used for search-and-rescue missions
Figure 1 shows the aerial-aquatic hybrid drone. The TJ-FlyingFish operates with complete autonomy, eliminating the need for human intervention throughout its expedition. During flight, all four units are positioned upward and rotate at high speeds. Upon landing on water, the units pivot downward and spin at a reduced speed, propelling the drone underwater. Its advanced cross-domain positioning and navigation system combines GPS, an inertial measurement unit, a depth meter, and a mini Doppler velocity log, enabling seamless autonomous control throughout its amphibious venture. This versatile drone finds utility in various fields, including aerial and aquatic surveys, remote sensing, and search-and-rescue missions, among a plethora of other applications. [1]
While the TJ-FlyingFish shares some similarities with traditional quadcopters, such as a central domed body and four arms, its design showcases distinctive features that set it apart. Notably, each of its four arms is equipped with a motor or propeller module, showcasing the drone's uniqueness. These propulsion units are specially designed with dual-speed gearboxes, enabling independent rotation to ensure optimal movement through air or water environments. This innovative design allows the TJ-FlyingFish to seamlessly adapt to its surroundings and maximize its efficiency in both aerial and aquatic operations. [1]
Professor Ben Chen said, “For propulsion, the operating range is switched for the different media by the dual-speed propulsion unit, providing sufficient thrust and also ensuring output efficiency. For thruster configuration, thrust vectoring is realised by the rotation of the propulsion unit around the mount arm, enhancing the underwater manoeuvrability.” [1]
Dives underwater for about 40 minutes per battery charge
This amphibious drone weighs 1.63 kilograms. It can hover for six minutes in the air or dive underwater for about 40 minutes per battery charge. It can dive to a maximum depth of three metres and move up to two metres per second in water. [1]
Professor Ben Chen added, “We are thrilled to unveil the TJ-FlyingFish, which represents a major milestone in our research efforts. We have simplified its structure and reduced its weight to ensure it can operate smoothly in water and sky media. We are excited to see how it will be used in the future.” [1]
Source: CHUK
References:
- https://www.cpr.cuhk.edu.hk/en/press/cuhk-announces-the-invention-of-an-aerial-aquatic-hybrid-drone/
- https://interestingengineering.com/innovation/unique-aerial-aquatic-hybrid-drone
Cite this article:
Hana M (2023), The Aerial-Aquatic Hybrid Drone, AnaTechmaz, pp.443

