Business Intelligence Trends in Data Governance
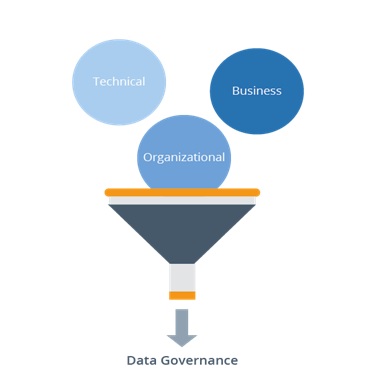
Figure 1. Business Intelligence Trends in Data Governance
Figure 1 shows Data governance is the specification of decision rights and an accountability framework to ensure the appropriate behavior in the valuation, creation, consumption and control of data and analytics. [1]
Other Definitions of Data Governance Include:
- “The exercise of authority and control (planning, monitoring, and enforcement) over the management of data assets.” (DAMA International)
- “A system of decision rights and accountabilities for information-related processes, executed according to agreed-upon models which describe who can take what actions with what information, and when, under what circumstances, using what methods.” (Data Governance Institute)
- “The specification of decision rights and accountability framework to ensure the appropriate behavior in the valuation, creation, consumption, and control of data and analytics.” (Gartner Glossary) [3]
The Current State of Data Governance
Today’s companies operate in a world where data is absolutely critical to business success, and the amount of data being produced is truly staggering. At the same time, they’re facing new data compliance requirements (GDPR and CCPA), as well as more complex consumer expectations around the use of their personal data.
Data-driven companies are embracing these data challenges by creating cross-functional teams and collaborative processes to manage their critical business data. They’re taking a policy-centric approach to data quality, data security, data accessibility, and data lifecycle management. And, as intelligent CRM systems become a reality, they’re employing powerful technology solutions to implement and enforce these policies. The end result is a new and better understanding of what data a company has, how it’s being handled, and how it can be used to drive the business forward. [2]
The Importance of Data Governance
Data governance provides clarity and safeguards against poor data management and non-compliance. IBM recently reported that in the U.S. alone, businesses lose $3.1 trillion every year due to poor data quality.
When data quality is low, it affects every aspect of a business, from marketing insights to financial planning, and hinders the achievement of important KPIs. It’s impossible to make accurate decisions or take calculated risks when data quality is poor. [4]
Data Governance
Search “definition of data governance” in Google or Bing, and you’ll find many explanations that are sometimes confused with data management. According to the Data Governance Institute (DGI), data governance is “a system of decision rights and accountabilities for information-related processes, executed according to agreed-upon models which describe who can take what actions with what information, and when, under what circumstances, using what methods.”
Gartner’s definition is the following: it encompasses a collection of processes, roles, policies, standards, and metrics that guarantee the efficient and effective use of information, allowing an organization to reach its goals. [4]
References:
- https://www.gartner.com/en/information-technology/glossary/data-governance
- https://www.dataversity.net/the-evolution-of-data-governance/
- https://www.dataversity.net/what-is-data-governance/
- https://www.delphix.com/glossary/what-is-data-governance
Cite this article:
Thanusri swetha J (2021), Business Intelligence Trends in Data Governance, pp. 21

